3 min read
Metallographic Analysis: Microstructure and Quality Control
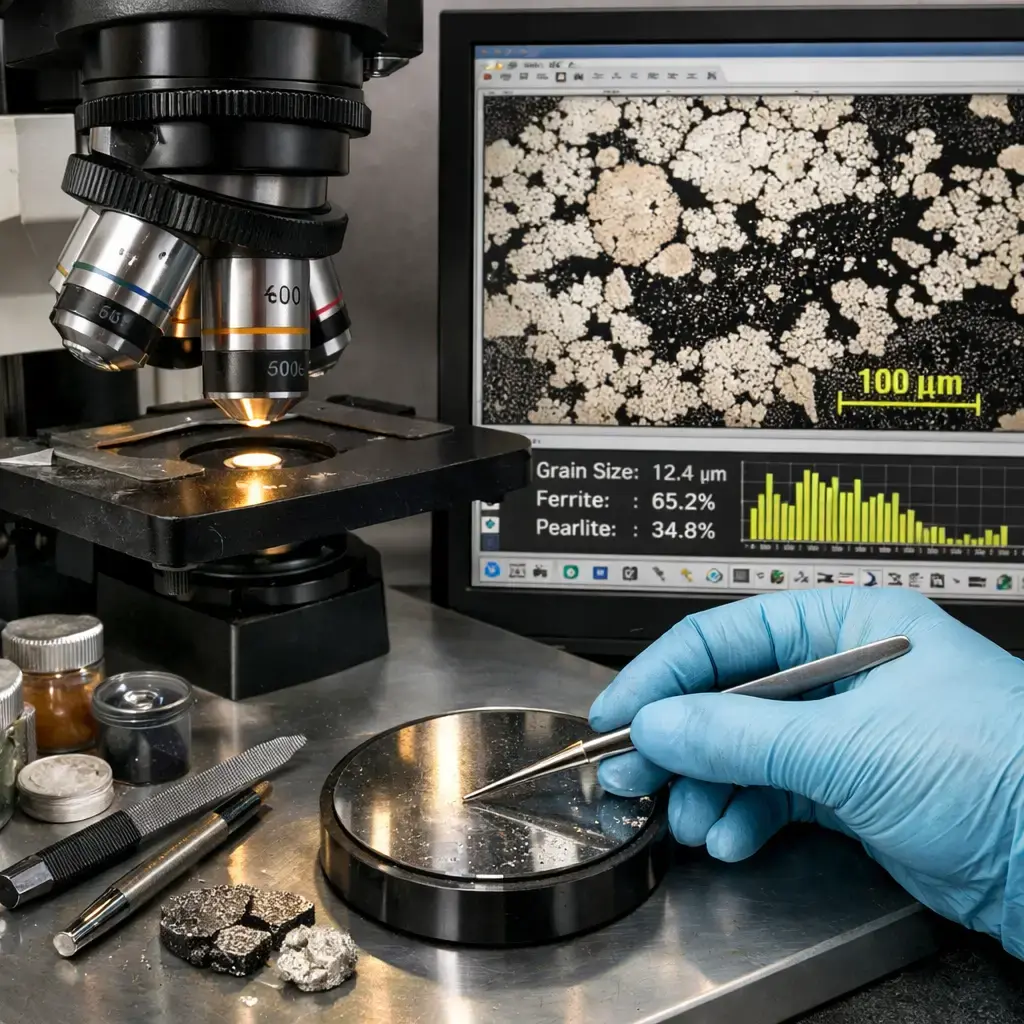
Metallographic analysis is a fundamental technique used to study the microstructure of metals and alloys. By observing a specially prepared sample...
2 min read
![]() Weerg staff
:
Aug 23, 2021
Weerg staff
:
Aug 23, 2021
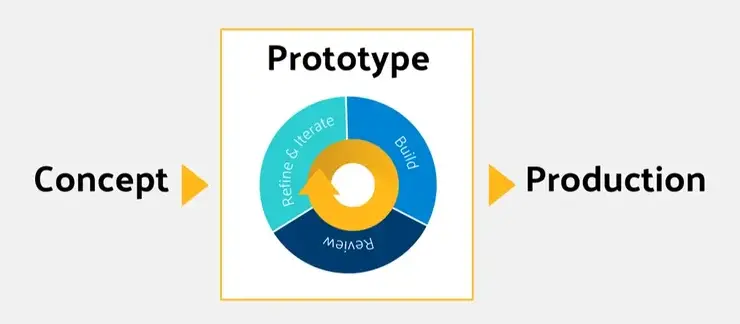
The arrival of 3D printing technologies and on-demand digital manufacturing has revolutionised product development, giving rise to the modern concept of Rapid Prototyping.
In the past, creating a prototype meant waiting 60–75 days and facing high costs.
Today, thanks to additive manufacturing, it is possible to obtain functional prototypes in 3–7 days, drastically reducing time, costs and development risks.
This updated 2026 guide explains everything you need to know about rapid prototyping:
Rapid prototyping includes a set of industrial technologies that allow the creation of a prototype directly from a 3D CAD file in extremely short timeframes.
The technologies are almost always additive, meaning they build the model layer by layer from raw material in the form of filament, resin or powder.
reduces lead times from 2–3 months to 3–7 days;
enables rapid iterations;
accelerates go-to-market;
reduces risks and development costs.
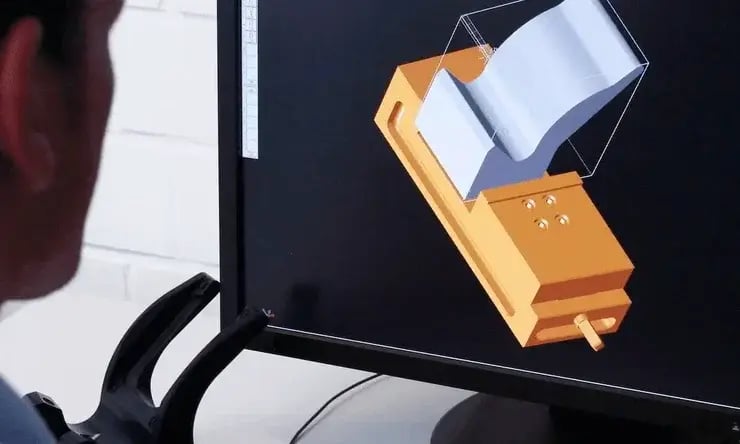

Prototyping is the phase in which a designer creates a physical model of their product to evaluate:
form
functionality
ergonomics
technical feasibility
component compatibility
The prototype is therefore the first real version of the project, useful for testing, modifications and validation before mass production.
| Method | Average lead time | Cost | Geometric complexity | Example technologies |
| Traditional prototyping | 60-75 days | High | Limited | Injection moulding |
| Rapid prototyping | 3-7 days | Low | High | MJF, FDM and MSLA 3D printing |
From months → to days.
Allows continuous iterations without slowing down the project.
A CNC or 3D-printed prototype costs a fraction of industrial tooling.
A digital model will never replace the physical perception of a real object.
It enables verification of:
ergonomics;
strength;
assemblies;
tolerances;
functionality;
mechanical performance.
Identifying a defect before production prevents thousands of pounds in wasted costs.

Used to evaluate:
shapes;
colours;
lines;
visual ergonomics.
Ideal technologies: SLA, MJF or high-resolution FDM.
Used to test:
loads;
strength;
movement;
assemblies;
tolerances;
real-world performance.
Ideal technologies: MJF, SLS, CNC, SLM/DMLS.
Used to confirm measurements, fittings and compatibility.
Exactly simulates the final product, including materials.

Rapid prototyping is cross-industry and is used in:
mechanics and automation;
automotive and motorsport;
eyewear and product design;
medical and biomedical;
electronics and consumer tech;
packaging and accessories.
It can be used in all phases of the production cycle:
concept and early design;
functional verification;
aesthetic mock-ups;
user testing;
events and presentations;
pre-production validation.

3D CAD design;
Selection of the most suitable technology;
Requirement analysis (aesthetic, functional, dimensional);
Rapid production (3D printing or CNC);
Post-processing (finishing, painting, treatments);
Testing and validation;
Iteration and improvement.
This cycle can be repeated several times until the perfect prototype is achieved.
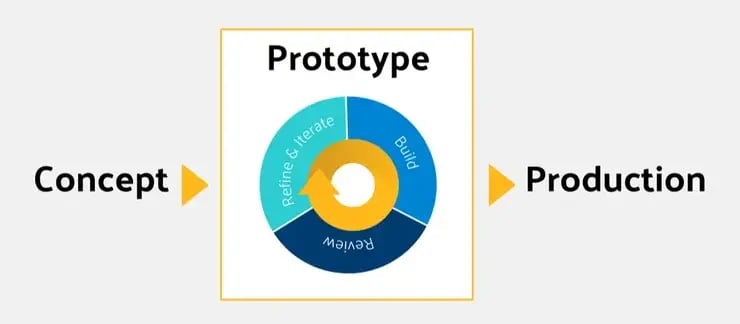
reduce thicknesses → less material;
lighten solid parts → add cavities and relief holes;
reduce model size;
optimise orientation to reduce build volume;
choose the technology best suited to the required level of detail.
An online service like Weerg allows you to:
upload a 3D file and obtain an instant free quote
produce prototypes in a matter of hours
achieve industrial-grade quality with no investment in machinery
receive finished parts extremely quickly
It is the ideal solution for those who want to accelerate product development with professional tools.

Rapid prototyping is an essential ally for modern product designers.
It allows ideas to be tested, improved and refined in a short time while reducing risks and costs.
Whether you are developing a mechanical part, a functional component or an aesthetic product, rapid prototyping enables you to:
validate ideas
speed up the process
optimise the design
obtain real-world feedback
reach the market faster

3 min read
Metallographic analysis is a fundamental technique used to study the microstructure of metals and alloys. By observing a specially prepared sample...
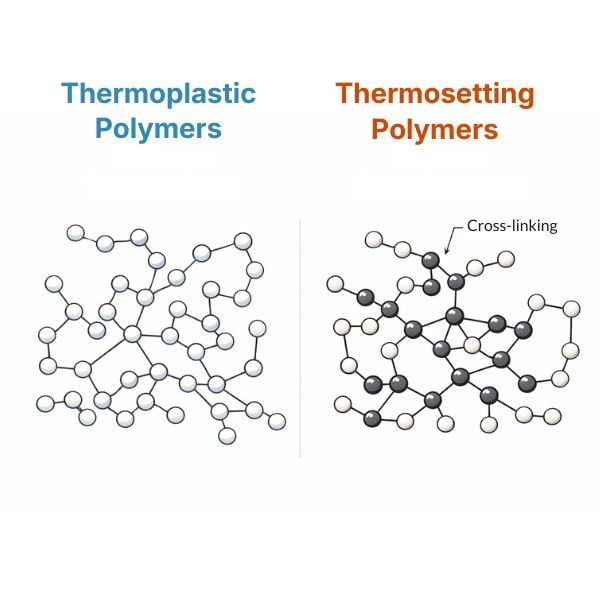
2 min read
Polymers represent one of the most versatile families of materials in modern industry. Within this category, the fundamental distinction is between ...
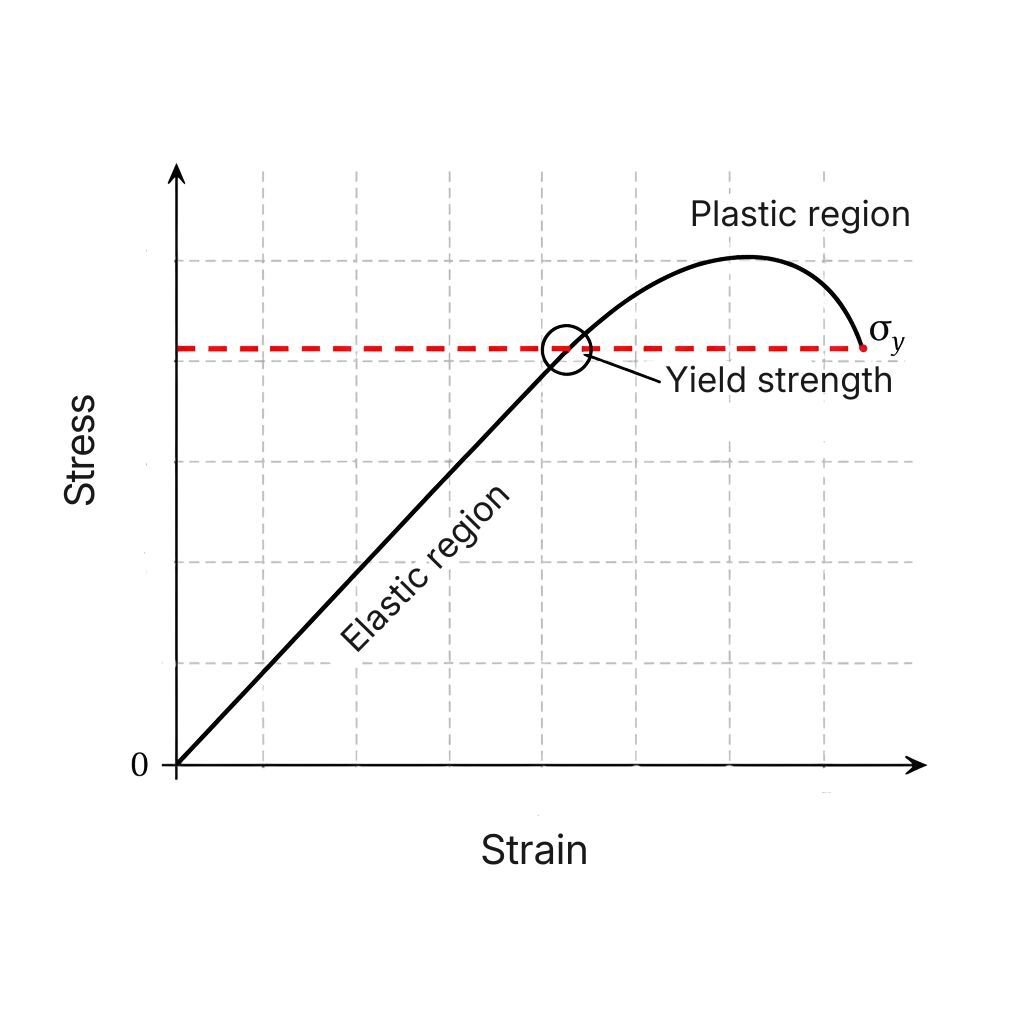
3 min read
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...