2 min read
Coefficient of Friction: what it is and why it is essential
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design because it affects wear, energy efficiency, accuracy, noise and component lifetime, both in industrial 3D printing and in CNC machining.
Understanding and controlling friction means reducing costs, increasing reliability and improving performance.
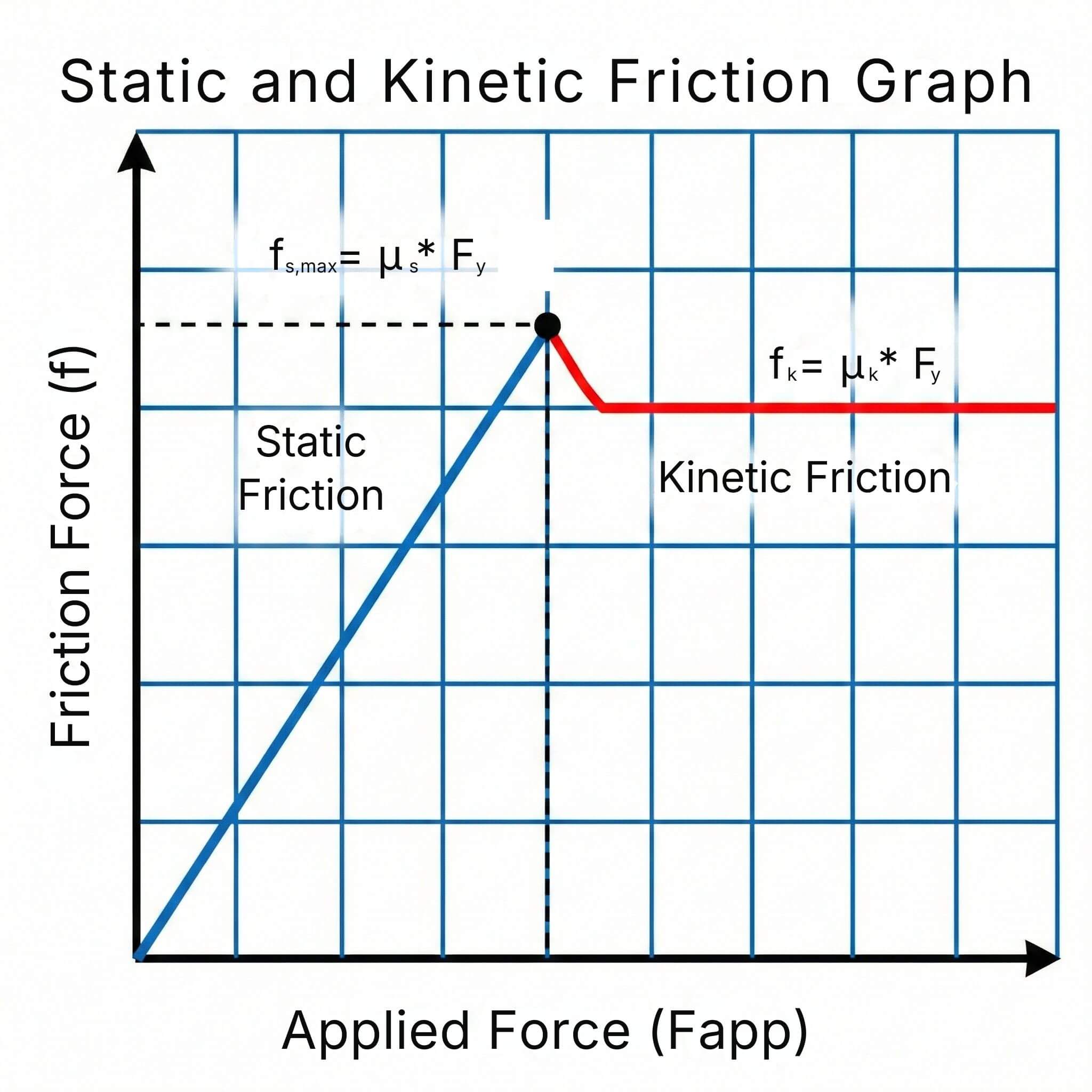
The coefficient of friction is a dimensionless value defined by the formula:
μ = Fₐ / Fₙ
Fₐ = friction force
Fₙ = normal force
μ high = more grip
μ low = smoother surfaces
Static friction (μₛ): prevents the start of motion
Kinetic (dynamic) friction (μₖ): acts during sliding
Rolling friction: typical of wheels and bearings, much lower

Values vary depending on surface roughness, load, lubrication and temperature.
In industrial 3D printing, friction also depends on the technology used:
MJF / SLS: uniform and isotropic friction
FDM: higher and directional friction
SLA: smooth surfaces but more brittle materials
For moving components, PA12 and PA11 produced with MJF offer the best balance between low friction and wear resistance.
Selection of low-μ materials (PA12, PA11, POM)
Improved surface finish
Lubrication or PTFE coating
Design that reduces contact pressure
Knurled or sandblasted surfaces
TPU and elastomers
Anti-slip patterns and functional geometries
The coefficient of friction directly affects:
Energy efficiency
Wear and service life
Mechanical accuracy
Safety and grip
Operating costs
Correct material and manufacturing process selection prevents over-engineering and long-term issues.
The coefficient of friction is a key parameter in the design of CNC components and 3D-printed parts. Materials such as PA12, PA11 and TPU allow controlled friction, high wear resistance and geometric freedom, making them ideal for modern industrial applications.
Do you need components with optimised friction?
The coefficient of friction is calculated as the ratio between the friction force and the normal force.
The formula is:
μ = Fₐ / Fₙ
where Fₐ is the friction force and Fₙ is the force pressing the surfaces against each other.
Static friction acts when the object is stationary and prevents the start of motion.
Kinetic friction acts during sliding and is generally lower than static friction.
It depends on:
the materials in contact
surface roughness
presence of lubricants
contact pressure
temperature and environmental conditions
It does not directly depend on the contact area.
In general, yes. Polymers such as PA11, PA12 and PTFE have lower coefficients of friction than metals, making them ideal for guides, bushes and moving parts.

2 min read
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...

3 min read
Nylon is one of the most widely used plastic materials in the world.Thanks to its combination of strength, light weight, flexibility and durability,...