3 min read
Metallographic Analysis: Microstructure and Quality Control
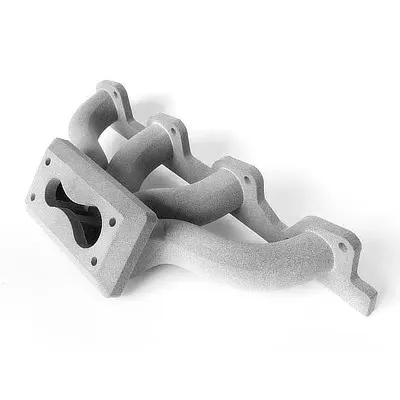
Metallographic analysis is a fundamental technique used to study the microstructure of metals and alloys. By observing a specially prepared sample...

Discovered by German chemist Karl Rehn and an Italian chemist Giulio Natta in the 1950s, polypropylene (PP) is one of the most spearheading plastics on the market today and is also used in 3D printing. From its high melting point, no reactiveness to water/detergents, crack resistance, and durability characteristics, it all equates to why polypropylene is fundamental in manufacturing.
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic material — that is, a polymer that can be heated and reshaped multiple times without losing its original properties.
It belongs to the polyolefin family and is produced by polymerising propylene, a petroleum derivative.
This process gives polypropylene its remarkable mechanical, chemical and physical properties, making it one of the most widely used plastics in the world.
Thanks to its lightness, strength, flexibility and thermal stability, polypropylene is highly valued across numerous industrial sectors.
What products are made from polypropylene? As the most common thermoplastics in the world, the uses of polypropylene are quite extensive. The benefits range greatly from packaging, developing plastic parts for machinery and equipment, and is even used in fabric/textile development. For some more example-driven insight, below are some key uses and the reasons behind them.
Why? Because PP is so flexible, cost-effective, and durable, it is often used for things like cladding, bumpers, interior components like dashboards, car batteries, and much more.

Why? The flexibility of polypropylene means it is an ideal “go-to” for a diverse range of packaging. With it being safe for food contact along with being chemically resistant, PP is often taken advantage of in three main sectors: tobacco, clothing, and food/confectionery packaging. Some of those include things like crates, bottles, jars for detergent and toiletries, and thin-wall containers for foods like yogurt cups.

Why? Since PP is more fire-resistant than wool, the fashion and sports industries use this plastic as well. Furthermore, given its resistance to environmental factors like sun, mold, water, and bacteria influences, PP is used for many outdoor appliances, sports-clothes equipment, undergarments, and accessories like tote bags.

Why? Going from fashion and food to medical, PP has also seen growth within the medical industry. With polypropylene BASF Ultrasint holding the ability to withstand chemically rich cleaning agents, disinfectants, solvents, and high temperatures, it makes it a reliable plastic for syringes, medical vials, specimen bottles, and pill containers. In summary, PP's applicational uses are subdivided into three categories: medical devices, packaging in general, and packaging systems for solid and liquid pharmaceuticals.

Why? There is a very promising chance there is PP in your home as we speak. Being the heat resilient, flexible, durable, and colorfastness material that it is, polypropylene is used in creating everyday consumer products like rugs, carpets, mats, microwave containers, plates, toys, and luggage. In addition, it can be found in many other in-house electronics like washing machines and dishwashers.
The best part is that regardless of the size and usage, this material offers incredible benefits that make it so widely sought out.
Polypropylene is produced through the polymerisation of propylene gas in the presence of catalysts.
The most famous and revolutionary are the Ziegler–Natta catalysts, which made it possible to obtain stereoregular polymers with superior mechanical properties.
Today, metallocene catalysts are also employed, allowing even greater control over the molecular structure and enabling the creation of PP grades with highly specific performance characteristics.
The resulting polymer can be processed into granules, fibres or thin films.
Thanks to its processing versatility, it can be used in various techniques such as injection moulding, extrusion, blow moulding, thermoforming and 3D printing.
This wide range of applications has made PP one of the most widely used materials in industrial manufacturing.
As you can see, Polypropylene (in Weerg we use PP/Polypropylene BASF Ultrasint printed with HP multi jet fusion technology) is used in just about every plastics market today. From products being used to protecting regular societal products to shielding medical equipment, it would be hard to imagine a world without this durable and versatile resource in it. Overall, polypropylene plastic has so many respected advantages, can save money, and offers reliable assurance that projects will have favorable long-term outcomes.
Sources and further reading
https://www.creativemechanisms.com/blog/all-about-polypropylene-pp-plastic
https://omnexus.specialchem.com/selection-guide/polypropylene-pp-plastic
https://www.thoughtco.com/what-is-polypropylene-820365
https://all3dp.com/1/polypropylene-pp-all-you-need-to-know/
https://www.plasticsmakeitpossible.com/about-plastics/types-of-plastics/professor-plastics-one-of-the-plastics-superheroes-polypropylene/
https://www.healthline.com/health/is-polypropylene-safe#is-it-bpa-free
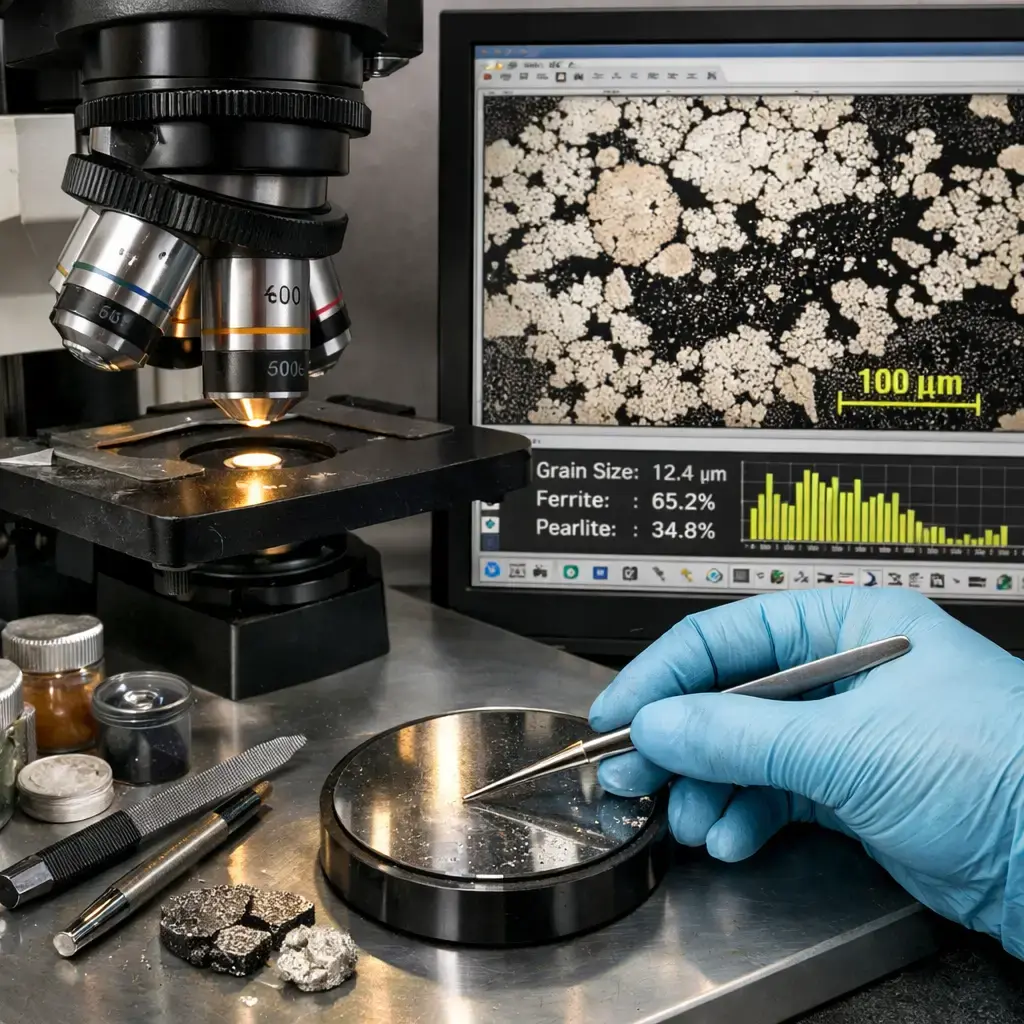

3 min read
Metallographic analysis is a fundamental technique used to study the microstructure of metals and alloys. By observing a specially prepared sample...
2 min read
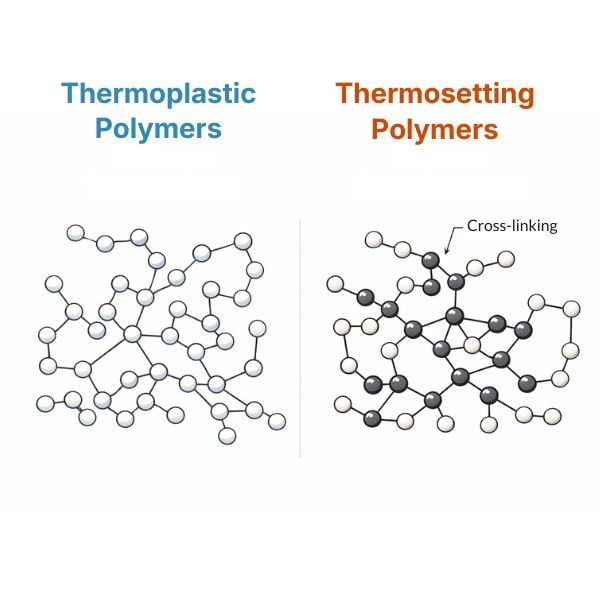
Polymers represent one of the most versatile families of materials in modern industry. Within this category, the fundamental distinction is between ...
3 min read
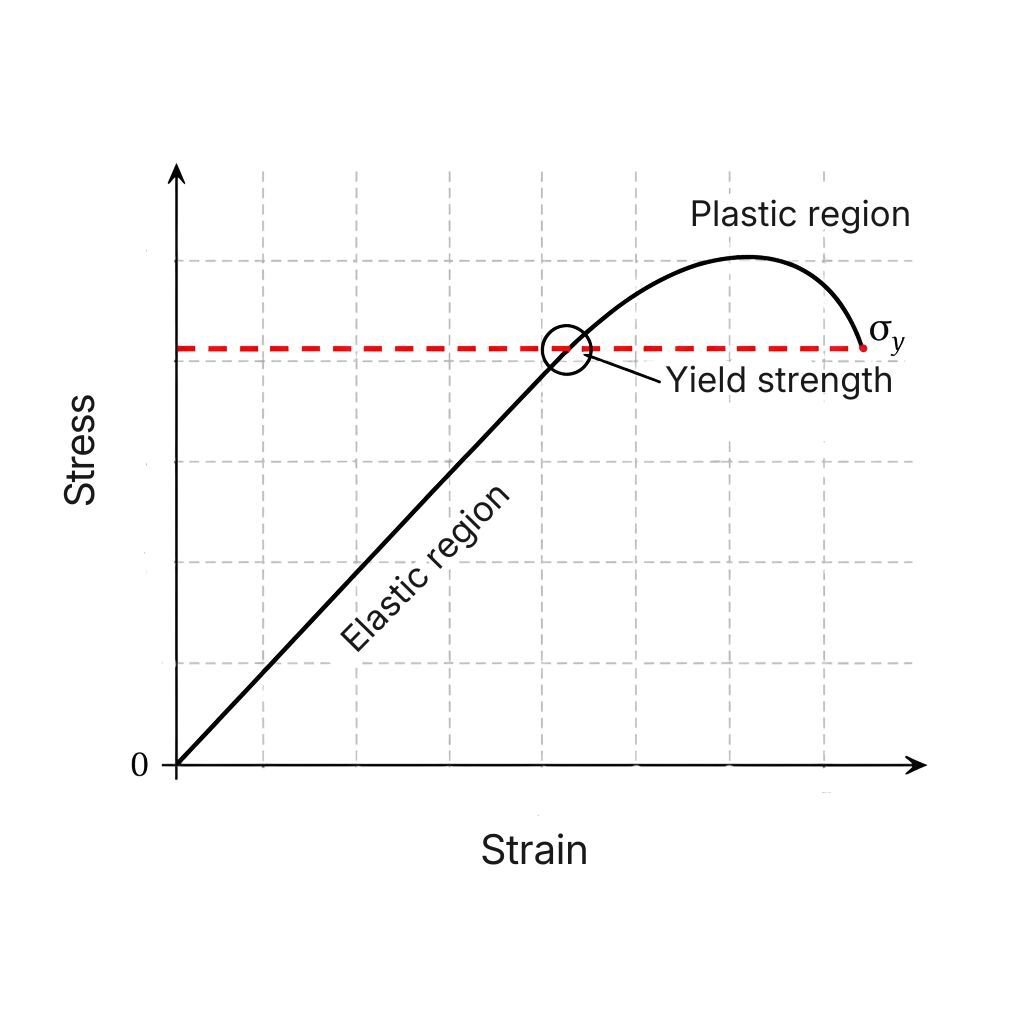
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...