4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
Polymers are everywhere: in everyday objects, electronic devices, synthetic fabrics, 3D printing materials, mechanical components, and even in our own bodies.
Despite their ubiquity, the concept of a "polymer" can seem abstract: what are they really? How are they formed? Why are they so versatile?
This guide offers a simple and comprehensive overview about:
What are polymers?
Where are polymers found?
How are polymers structured?
Main types of polymers
Properties of polymers
How are polymers produced?
Polymers and 3D Printing
Applications of polymers
A polymer is a macromolecule formed by the repeated union of smaller units called monomers.
The term comes from the Greek polýs (many) and méros (parts).
In other words: a polymer is like a chain composed of many molecular "links" joined together. The length of the chain, the type of monomer, and the structure all influence the final properties of the material.
Polymers can be:
Already present in nature, such as:
DNA
Cellulose
Natural rubber
Proteins
Starch
Man-made, such as:
Polyethylene (PE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polystyrene (PS)
Nylon and polyamides
PVC
Epoxy resins

The molecular structure determines the characteristics of the material. There are three main schemes:
These soften with heat and can be remoulded multiple times. Examples:
Perfect for: 3D printing, extrusion, and injection moulding.
Once hardened via a chemical reaction, they cannot be remelted. Examples:
Epoxy resins
Polyurethane resins
Bakelite
Key feature: They resist heat and solvents very well.
Highly elastic materials that return to their original shape after deformation. Examples:
Rubber
Silicone
Useful for: Gaskets, wheels, flexible components, and shock absorbers.
Polymers are so widespread because they can assume vastly different characteristics:
Lightweight
Impact-resistant
Thermal and electrical insulators
Flexible or rigid
Easy to process
Cost-effective
Chemically resistant
Stable over time
By modifying the composition, structure, and additives, it is possible to obtain materials with tailor-made performance.

Polymers are obtained through polymerisation, a chemical process that joins monomers into long chains. There are two main methods:
3D printing utilises a vast array of polymers thanks to their processability and versatility.
FDM primarily uses:
PLA
ABS
PETG
Nylon
Reinforced composites
MJF/SLS use:
PA12, PA11 (among the highest-performing technical polymers)
TPU for flexible parts
PP (Polypropylene)
SLA/MSLA use:
Photopolymer resins
Ceramic resins
"Tough" or "ABS-like" resins
Technical polymers are making it possible to produce functional, durable, and high-performance components.
Polymers are practically everywhere:
Polymers are an incredibly versatile class of materials, capable of offering bespoke solutions for almost every industrial sector.
Thanks to chemistry, material engineering, and 3D printing, polymers continue to evolve, opening up new possibilities in terms of design, performance, and sustainability.
Do you want to manufacture polymer components with industrial quality?
Upload your 3D file and choose the material best suited to your project

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
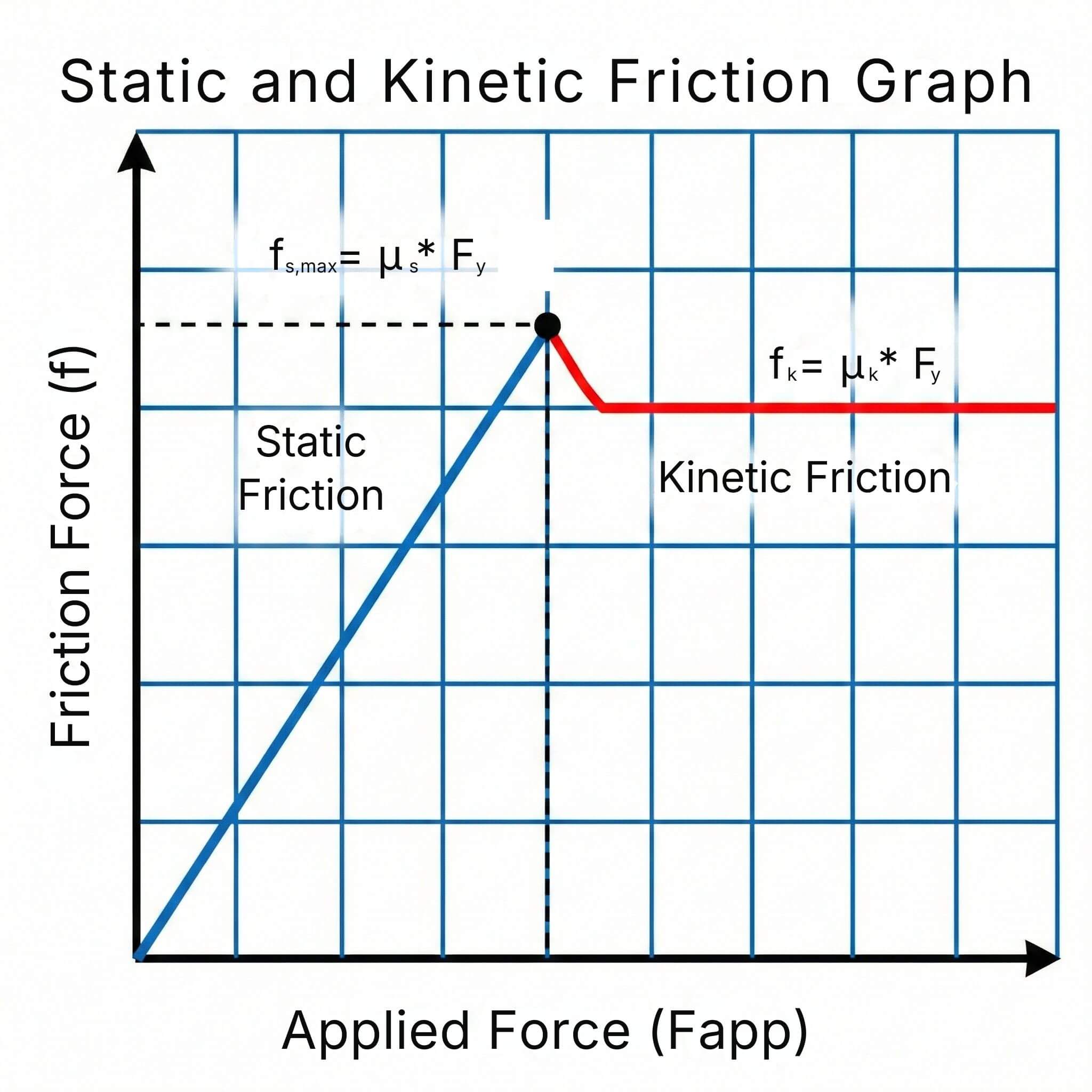
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...