3 min read
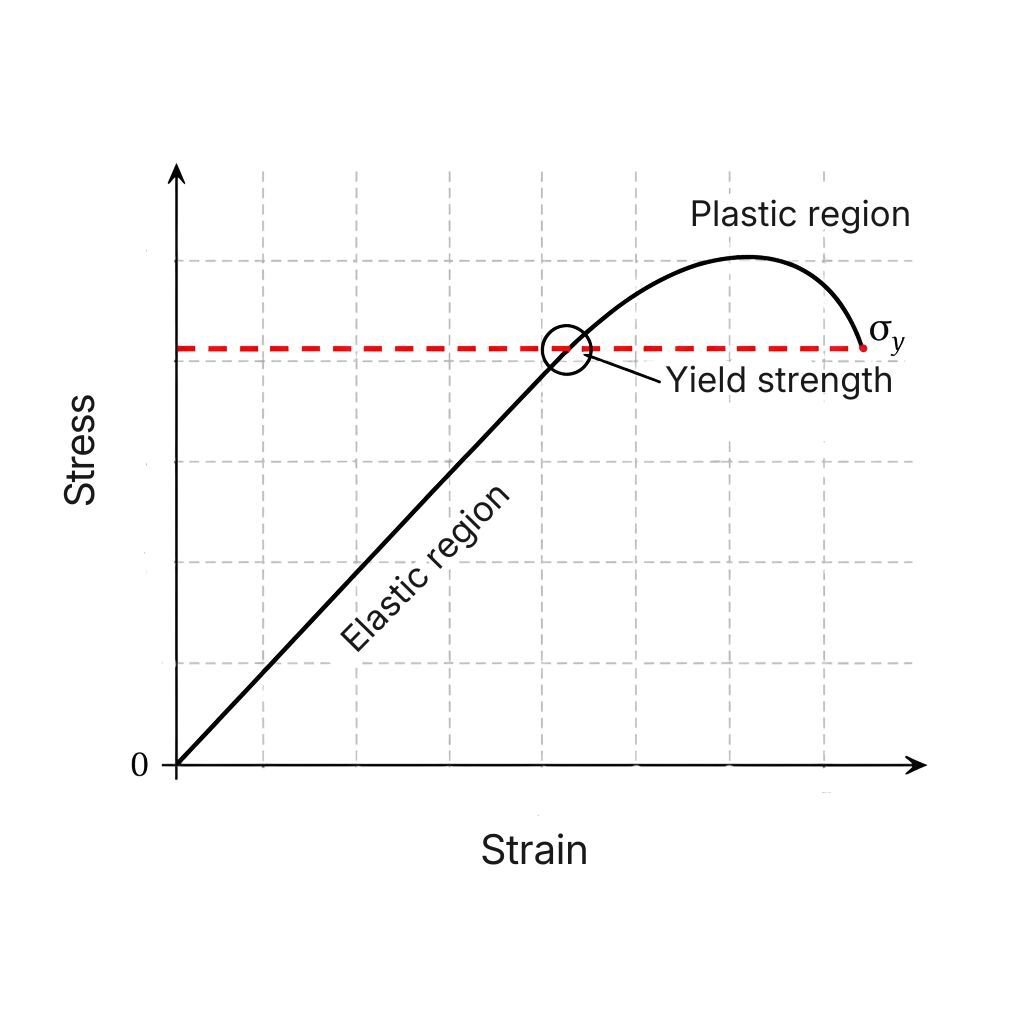
Yield Strength: Elastic Limit of Materials
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...

When it comes to selecting materials for CNC machining, steel and aluminium stand out as two of the most common options, each with distinctive characteristics that influence design and production decisions. Understanding the differences between these two metals is essential for optimising performance, costs, and production efficiency.
In this guide we analyse steel vs aluminium in terms of:
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, often enriched with elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum or vanadium to improve its properties.
Common types:
Carbon steel → a good compromise between strength and cost.
Stainless steels (AISI 304, 303, 316, 316L, etc.) → excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for harsh environments or food/chemical applications.
In general, steel is:
strong and versatile
suitable for structural and mechanical applications
available in a very wide range of alloys for specific requirements
Aluminium is a light and soft metal, almost always used in alloy form to increase its strength.
The most common alloys:
Aluminium 6061 → highly versatile, good mechanical strength, excellent machinability; used in many sectors.
Aluminium 7075 → one of the strongest alloys, used in aerospace, military, racing.
Other alloys (5052, 6082, etc.) → for marine applications, lightweight structures, CNC-machined components.
Aluminium is:
very lightweight
naturally corrosion resistant thanks to its thin protective oxide layer
ideal for components where weight is critical
The most obvious difference is weight:
Aluminium is therefore about three times lighter than steel.
This difference is crucial in sectors such as:
With Weerg you can take advantage of:

In absolute terms, steel generally offers higher mechanical strength than aluminium.
Aluminium has lower strength than steel, but an excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
In practice:
Aluminium is naturally corrosion resistant thanks to a protective oxide film that forms on its surface.
It is therefore excellent for:
Non-stainless steel tends to corrode unless protected (painting, galvanisation, treatments).
For aggressive environments, the following are used:
Alternatively:
Aluminium is generally easier to machine:
Steel:
With advanced machinery (such as Weerg’s 5-axis CNC machining), it is still possible to achieve:
Generally:
Aluminium:
Both steel and aluminium are highly recyclable and fit well within a circular economy framework.
Specifically:

Choose steel if:
Steel is the natural choice for:
Choose aluminium if:
It is the ideal material for:
The choice between steel and aluminium always depends on the specific requirements of the project:
Steel → robustness, durability, cost-effectiveness, high loads and stresses.
Aluminium → lightness, corrosion resistance, excellent machinability and power-to-weight performance.
Thanks to Weerg’s advanced CNC machining, you can make the most of the properties of both materials, obtaining components that are precise, repeatable and optimised for real-world use.
UPLOAD YOUR FILE NOW AND HAVE YOUR STEEL OR ALUMINIUM COMPONENTS CNC MACHINED
3 min read
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
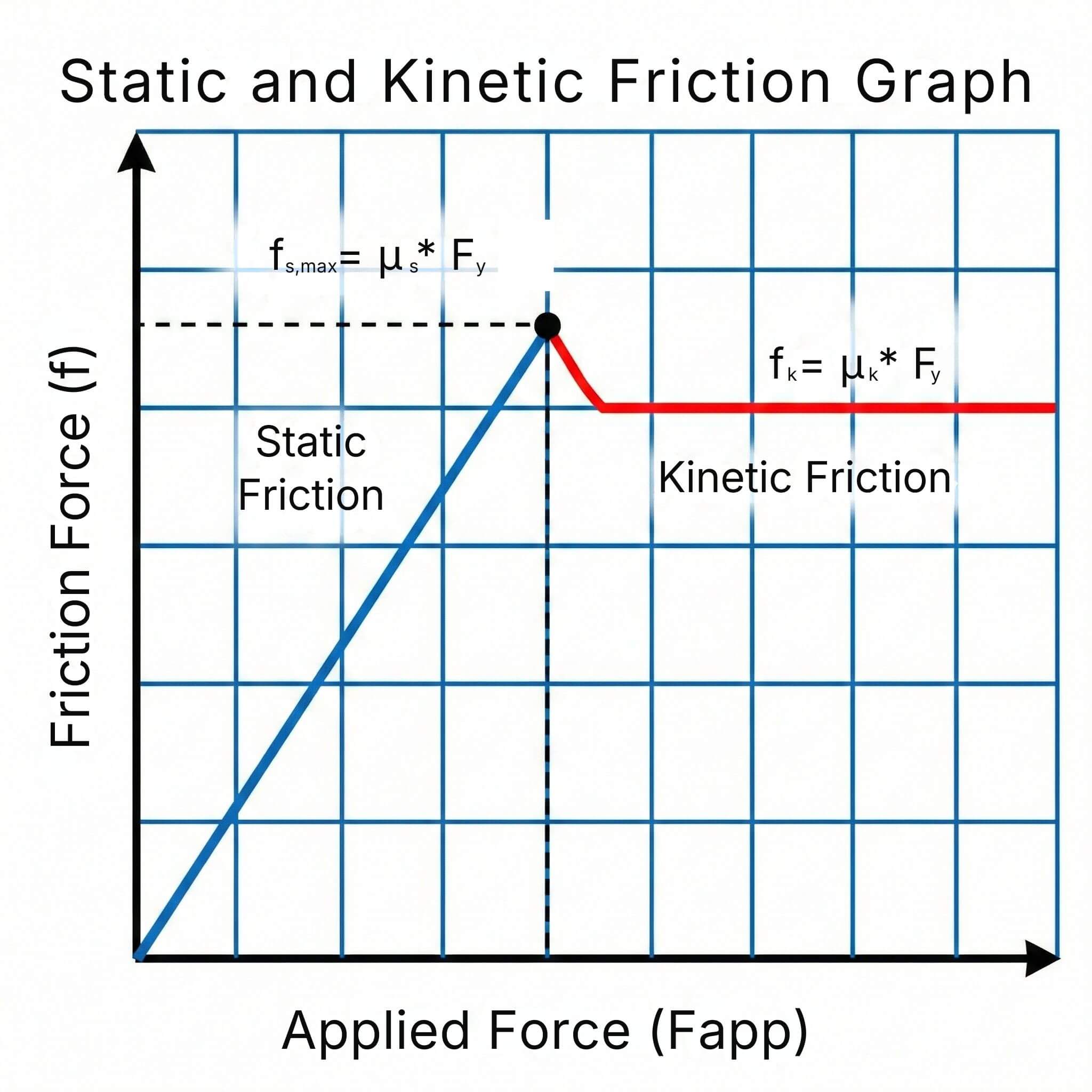
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...