4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...

Since the birth of 3D printing in the 1980s and through to today’s modern industrial processes, additive manufacturing has made enormous progress.
Among the most widespread and representative technologies today are:
In this guide, we examine the differences, advantages, materials, applications and limitations of the two technologies, to help you choose the ideal one for your project.
This is the most widespread 3D printing technology among hobbyists, designers and small workshops.
It uses a thermoplastic filament that is melted and extruded through a nozzle, building the part layer by layer.
It is easy to use, inexpensive (consumer printers from €100–200) and ideal for quick prototypes and concept testing.
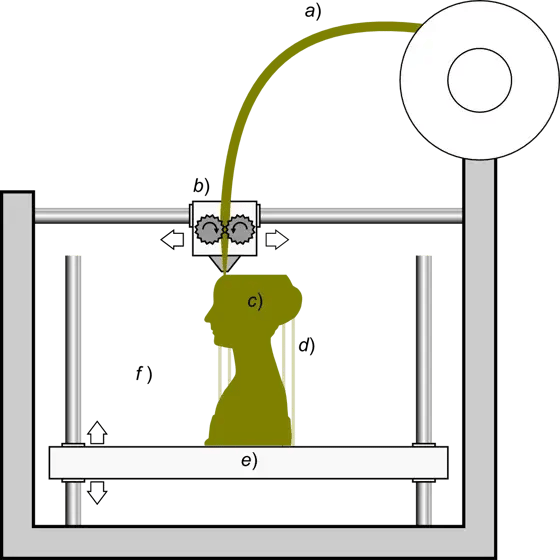
In FDM technology, a filament a) of plastic material is fed through a heated moving head b) which melts and extrudes it, depositing it, layer by layer, in the desired shape c). A mobile platform e) lowers after each layer has been deposited. For this type of 3D printing technology additional vertical support structures are required d) to support the protruding parts. Source: Wikipedia by Paolo Cignoni
This is a professional technology developed by HP and introduced in 2016.
It uses a nylon powder bed and an inkjet array that selectively deposits fusing and detailing agents, which are then melted by IR lamps.
The result?
Isotropic, strong parts, support-free, with quality comparable to injection moulding.

One of 12 HP Multi Jet Fusion printers installed by Weerg. Get an instant quote.
The 3D model is “sliced” using software (Cura, PrusaSlicer).
The printer melts the filament and deposits it through a nozzle.
Each layer solidifies before the next one is added.
Supports are required for overhangs.
Typical layer height: 0.1–0.5 mm.
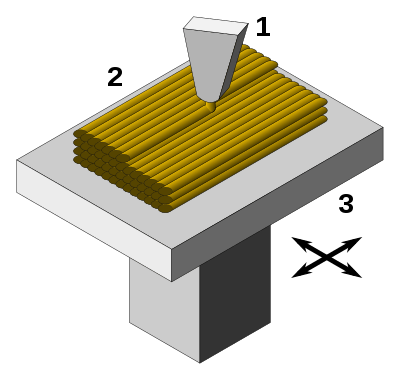
Printing process: 1 - Print extruder, 2 - Deposited material, 3 - Construction plan.
Source: Wikipedia by Paolo Cignoni
A roller spreads a thin layer of powder.
Inkjet heads deposit fusing and detailing agents.
An IR lamp selectively melts the powder.
The surrounding powder supports the part → no supports required.
At the end of the print, the build box is removed and the parts are cleaned.
MJF productivity is approx. 300 cm³/h, compared with approx. 10 cm³/h for FDM.
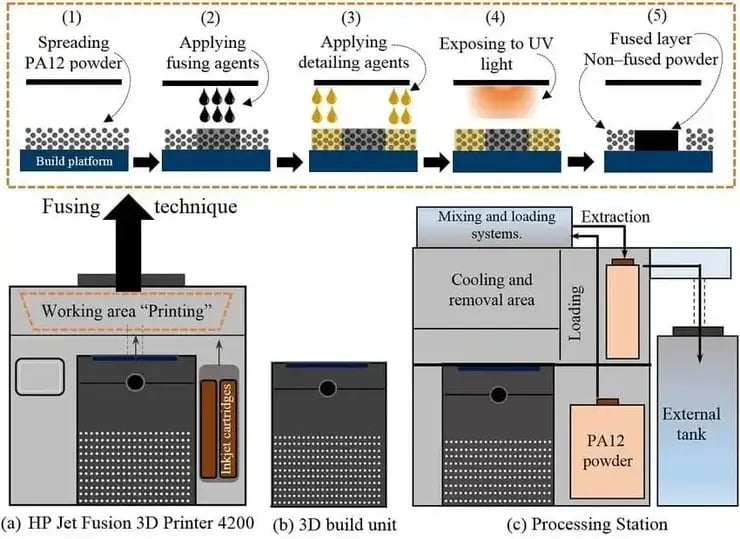
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) process scheme: (a) stages 1-5 of the fusion process); (b) 3D construction unit; (c) processing station. Source: research gate
Most commonly used:
PLA → easy, good aesthetics, biodegradable
ABS → strong but prone to warping
PETG → balance between strength and ease of printing
TPU → flexible
Nylon → strong but difficult to print
Professional FDM printers (from €25,000) can print high-performance materials:
PEEK, Carbon PEEK, Ultem, advanced composites
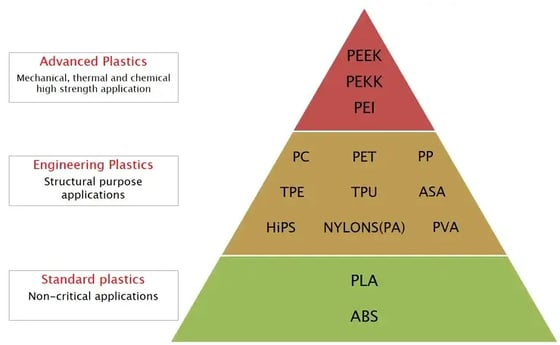
FDM printing offers a good range of materials. Source filament to print
MJF processes high-performance industrial materials, including:
PA12
PA11
PA12 GF (glass-filled)
TPU
PP (Polypropylene)
These materials offer mechanical properties very close to injection moulding.
FDM: visible layers, rough surface
MJF: uniform, “velvety”, professional finish
FDM: variable, depends on the printer
MJF: very high and repeatable
FDM: anisotropic → weakness along the Z-axis
MJF: isotropic → consistent strength in all directions
FDM: limited in fine details; requires supports
MJF: excellent detail, no supports, ideal for complex geometries

FDM printing farm: the Prusa printing farm has over 300 FDM printers in a single room
rapid prototyping
concept models
low-cost, non-functional parts
experimentation with special materials
Perfect for: makers, students, designers in the early stages of development.
strong, functional prototypes
small and medium-batch production
technical components
mechanical parts, snap-fits, housings
complex geometries without supports
Perfect for: engineering, automotive, medical, robotics, advanced manufacturing.
Advantages
inexpensive
easy to use
wide material variety
excellent for early prototypes
Disadvantages
low precision
poor surface aesthetics
limited repeatability
common issues: warping, clogging, delamination
supports always required
Advantages
industrial-grade quality
isotropic, strong parts
no supports
high productivity
uniform finish
ideal for end-use production
Disadvantages
higher cost compared with FDM
fewer materials
requires industrial equipment (≈€500,000)
| Characteristic | FDM | MJF |
|---|---|---|
| Surface quality | ★★☆☆☆ (visible layers) | ★★★★☆ (uniform, fine) |
| Accuracy | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Mechanical strength | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★★ (isotropic) |
| Materials | Very varied | Industrial, high-performance |
| Supports | Required | None |
| Production speed | Slow (10 cm³/h) | Very fast (300 cm³/h) |
| Repeatability | Medium | High |
| Printer cost | €100–25,000 | ~€500,000 |
| Applications | Prototypes, hobby | Functional prototypes, production |
The real question is not “which technology is better?” but rather:
Which technology is better for your purpose?
Choose FDM if:
you have a limited budget
you need fast, low-cost prototyping
material variety is important to you
Choose MJF if:
you need strong, functional parts
you require industrial-grade quality
you need small/medium-batch production
you want complex geometries without supports
MJF is currently one of the most significant advances in industrial 3D printing, capable of competing with injection moulding in cost, speed and performance.

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
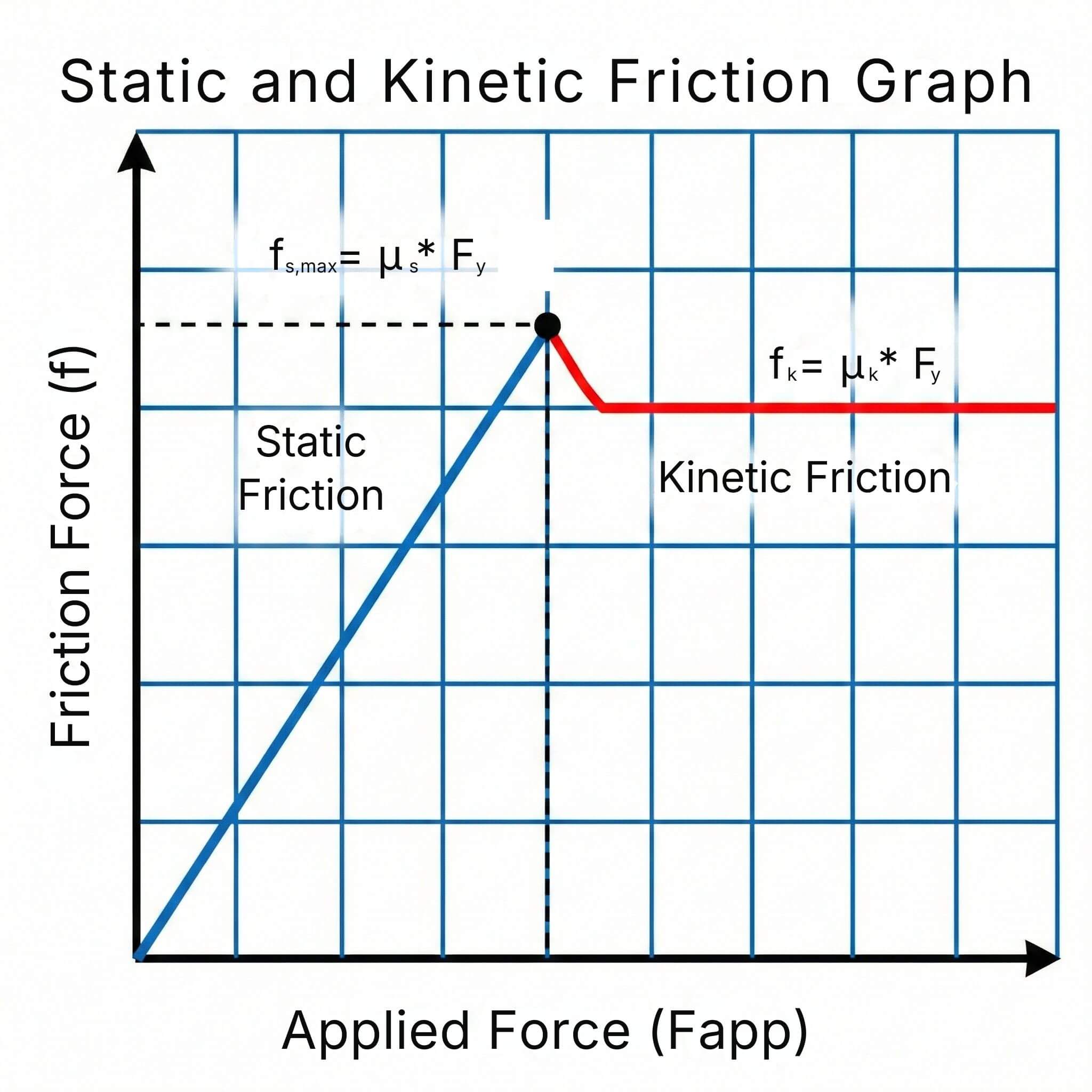
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...