4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
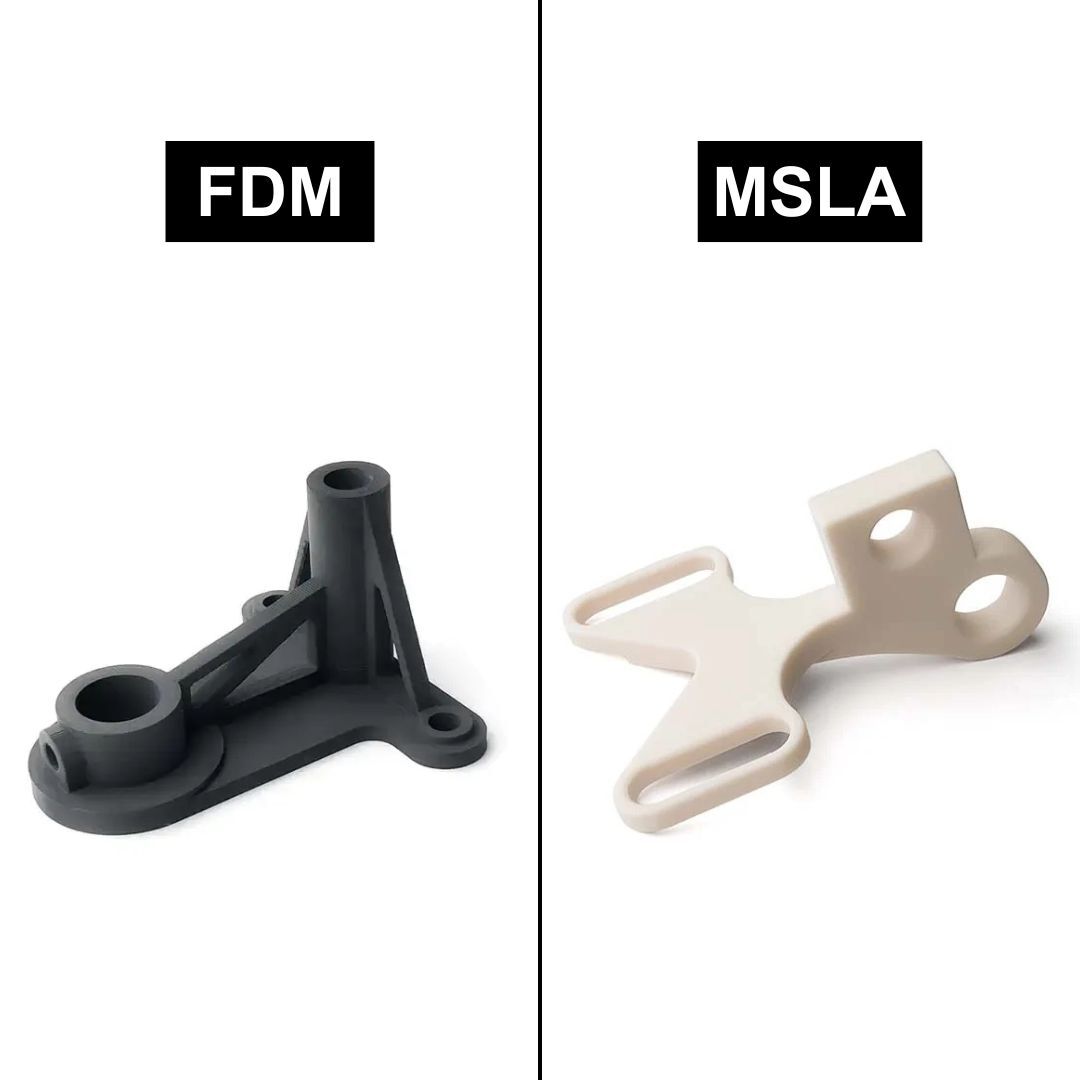

If you’re starting out with 3D printing, or you need to select the best technology for a professional project, you’ve probably asked yourself: Is filament (FDM) 3D printing better, or resin (SLA/MSLA)?
Both are excellent technologies, but they differ greatly in terms of quality, materials, costs, performance, and intended use.
In this updated 2026 guide, we analyse differences, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases so you can make an informed choice:

Resin 3D printing uses UV light (laser, LCD, or projector) to cure a liquid photopolymer resin, creating objects with extremely high surface quality.
the resin is exposed to UV light
the light selectively cures each layer
the object is “lifted” from the vat as it grows
Standard (high definition)
ABS-like (stronger)
Tough (impact resistant)
Flame retardant/ High temperature (thermal resistant)
Ceramic-like (premium matte finish)
exceptional detail
smooth, clean surfaces
ideal for miniatures, modelling and aesthetic objects
tight tolerances
excellent reproduction of micro-details
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) is the most widespread technology worldwide, thanks to the availability of affordable printers and ease of use.
a plastic filament is heated
extruded through a nozzle
deposited layer by layer
the object forms on the build plate
PLA (easy, inexpensive, aesthetic)
ABS (strong, but prone to warping)
PETG (great all-rounder)
TPU (flexible)
Nylon and reinforced fibres (advanced level)
very low cost
wide variety of materials
perfect for rapid prototyping
easy to use
visible layer lines
limited precision
less smooth surfaces
strong anisotropy (weak Z-axis)
requires supports and post-processing

Here’s a clear overview of the main differences:
| Aspect | FDM Printing | Resin Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Surface quality | Medium, visible layers | Very high, smooth surfaces |
| Detail | Good | Excellent |
| Mechanical strength | High (with technical materials) | Medium (some tough resins are good) |
| Available materials | Many | Fewer |
| Printing cost | Low | Medium |
| Post-processing | Support removal + sanding | Washing + post-curing |
| Safety | High | Requires PPE and ventilation |
| Speed | Good | Excellent with new-generation LCD |
Resin printing is the right choice for:
FDM is perfect if you want:
It depends on the purpose:
Choose FDM if you want:
low costs
many materials
quick prototypes
strength and functionality
Choose resin if you want:
perfect surfaces
very high detail
miniatures or models
premium aesthetic prototypes
high precision
Conclusion:
FDM wins for cost and functionality.
Resin wins for aesthetics and precision.
For professional work, the choice depends on the project:
Design | Modelling: resin
Mechanical | Functional parts: FDM with technical materials
Aesthetic prototyping: resin
Cost-effective production: FDM
Extreme detail: resin
Technical strength: Nylon/Carbon FDM or industrial technologies like MJF
Choosing between filament and resin 3D printing depends on the project type, the required level of detail, the desired mechanical properties, and the budget.
Both technologies are excellent, but for different contexts.
Upload your file to Weerg and choose the technology that best suits your project

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
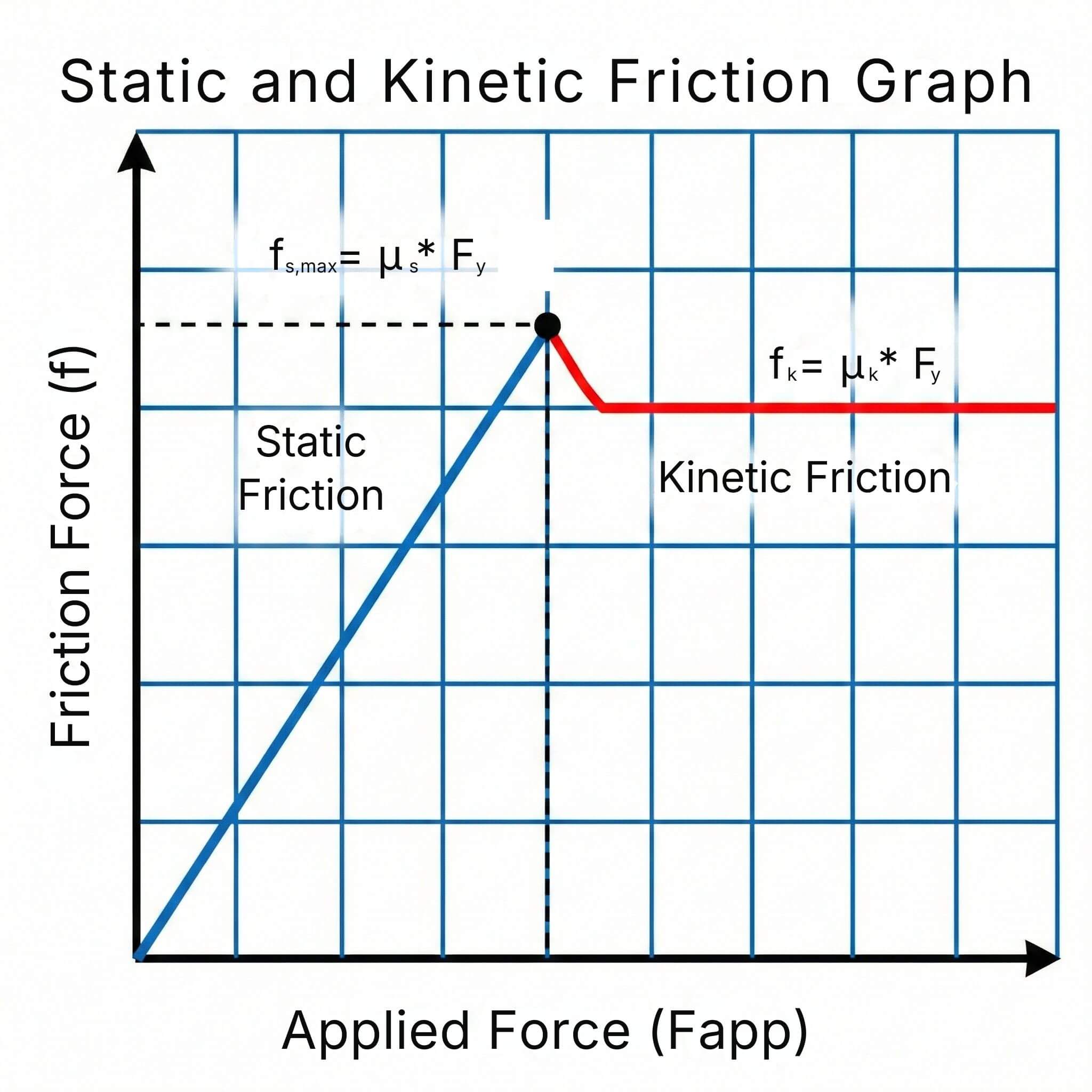
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...