2 min read
Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Polymers: Differences and Uses
Polymers represent one of the most versatile families of materials in modern industry. Within this category, the fundamental distinction is between ...

Aluminium has become a very popular material for applications across many different industries and in CNC machining. Its popularity over other materials is associated with its excellent mechanical properties. If you want to learn all about the top 3 aluminium alloys, keep reading as we disclose all the details.
Aluminium is a metallic material with silver or matte grey colour. The latter usually depends on the surface roughness.
One of the main reasons for using aluminium across different industries is that it is lightweight, ductile, and malleable.
Other relevant properties of the top aluminium alloys, are the following:
Also, aluminium does not create magnetism issues and it is not flammable.
On the other hand, aluminium alloys have a couple of disadvantages that you must consider. These disadvantages are:
Now that we know a bit more about aluminium, it is time we discover the top 3 aluminium alloys.

There are a number of aluminium alloys in the current market. Yet, we truly believe there are 3 that excel above the rest for most applications. These are aluminium 7075, aluminium 5083, and aluminium 6082. Let’s see each of them in more detail.
Aluminium 7075 is well-known for its excellent fatigue strength. This alloy has better corrosion resistance than the aluminium 2000 alloys. Most times, machine operations are conducted using oil lubricants.
The primary element found in the 7075 aluminium alloy is zinc. With zinc as the top alloying element, this aluminium grade obtains a series of properties that make it suitable for a wide variety of applications.
However, this aluminium alloy is not easily weldable, and it may be considered too costly for some applications.
The main properties of the 7075 aluminium alloy are:
Aluminium 7075 applications
The 7075 aluminium alloy is a great solution for applications that require lightweight components with the highest level of strength possible. Also, the 7075 aluminium alloy allows to achieve very complex geometries with high precision. Common applications for 7075 aluminium parts include but are not limited to:
Because of the cost, you should only use it if your specific application requires the essential features of this alloy. Otherwise, you may be better off with a cheaper alloy.
Possible treatments after machining 7075 aluminium
This is an aluminium alloy that accepts different types of treatments after machining. The most common treatments include heat treatment, annealing, and ageing. However, anodizing is not a possible treatment after machining 7075 aluminium.
The aluminium 5083 alloy is popular due to having exceptional performance in extreme environments, such as exposure to seawater and industrial chemical environments.
The 5083 alloy is also exceptional for welding since it does not lose strength during the process. In addition to a very high resistance, it is recommended for use at temperatures up to 600°C.
Other relevant properties of the aluminium 5083 alloy include:
Aluminium 5083 applications
As it was mentioned above, the aluminium 5083 alloy is excellent in applications that require resistance to harsh environments. Therefore, the main applications for this alloy are associated with that aspect.
Aluminium 5083 alloys are mainly used in:
Given the properties, you should consider this aluminium alloy whenever exposure to the types of environments above is not avoidable. Another important factor to select is the need for high mechanical strength and fatigue resistance, as long as the part does not operate at very high temperatures.
Possible treatments after machining 5083 aluminium
This aluminium alloy allows different treatments to be used on the machined part. The most common ones include:
The aluminium 6082 alloy is mainly known for offering increased resistance when compared to the 5xxx series alloys.
This is the strongest alloy in the 6xxx series, and it is often called structural aluminium alloy since it is very popular for structural components.
The main reason for this alloy to be so strong while having very high corrosion resistance is that it contains a large amount of manganese which controls the grain structure, thus making it more stable.
Perhaps the only negative characteristic of the aluminium 6082 alloy is that thin walls are difficult to machine as well as complex shapes are difficult to achieve via extrusion. Also, while it accepts welds, it is important to consider that the welded zone will lose strength.
Yet, it is a very recommended substitute to low carbon steels, especially when the high corrosion resistance is needed.
Aluminium 6082 applications
We already mentioned that the aluminium 6082 alloy is widely used in structural components such as trusses and bridges. But of course, this could not be the only application for a material with such properties as those mentioned above. Machinery components are also commonly made with this aluminium alloy.
Common applications for the aluminium 6082 alloy include:
Possible treatments after machining 6082 aluminium
The aluminium 6082 alloy is very versatile, and it also accepts different treatments to make it even more suitable for specific cases.
The most common treatments used after machining this alloy are:
There you have it, these are the top 3 aluminium alloys, their properties and applications.
With this information you should be capable of making a smarter selection for your specific application.
However, if you are still in doubt, the recommendation is to consult an expert. Do not hesitate to contact us, we will be more than glad to help you!
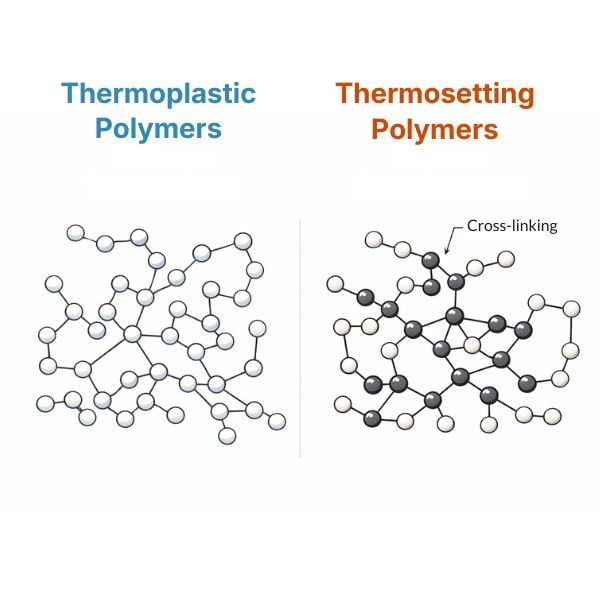
2 min read
Polymers represent one of the most versatile families of materials in modern industry. Within this category, the fundamental distinction is between ...
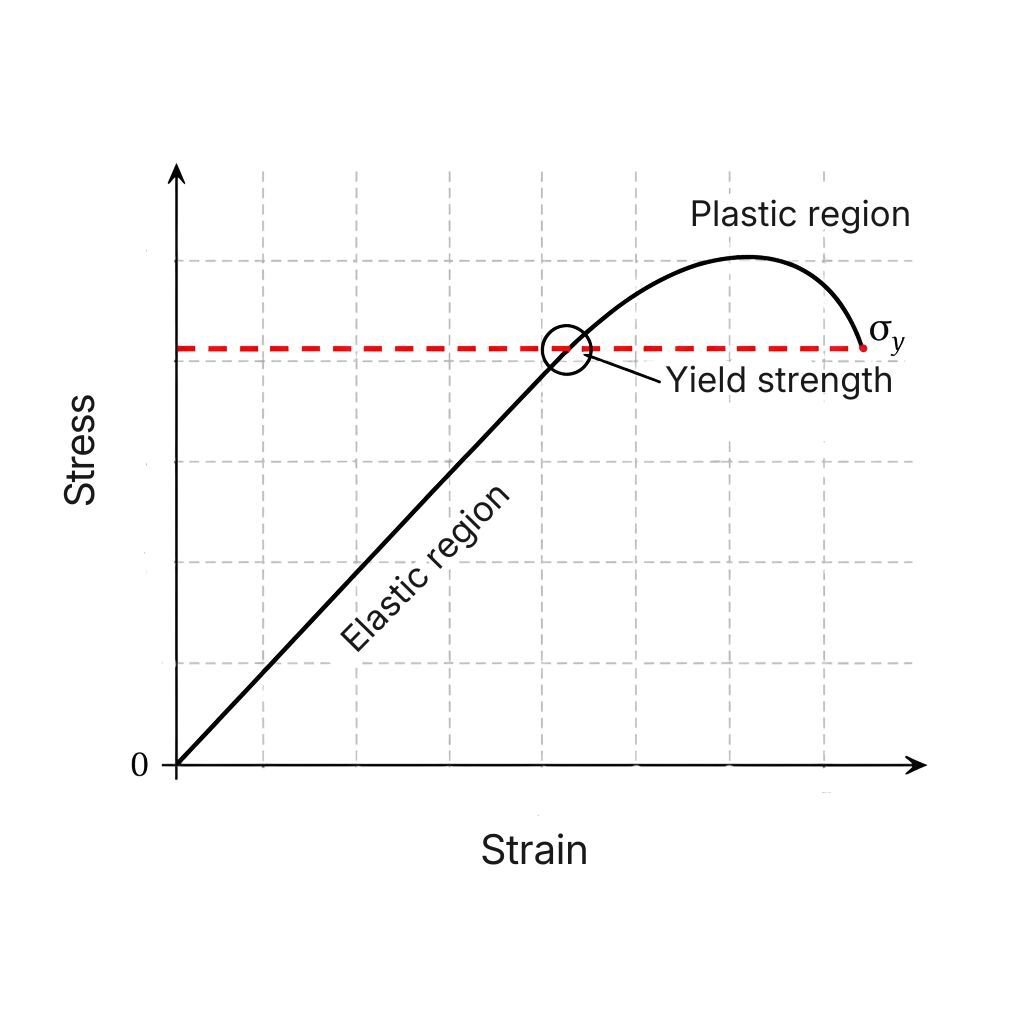
3 min read
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...