3 min read
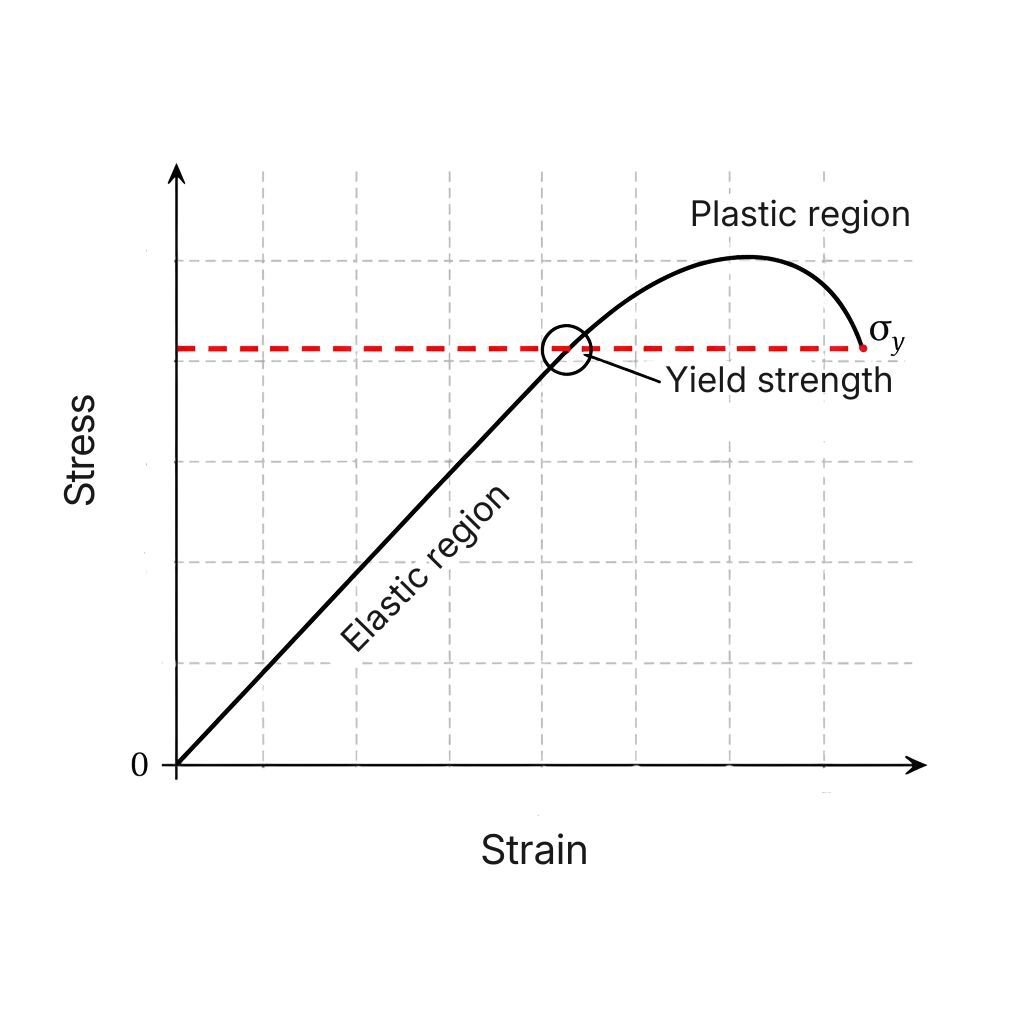
Yield Strength: Elastic Limit of Materials
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...
3 min read
![]() Fabio Trotti
:
Sep 15, 2021
Fabio Trotti
:
Sep 15, 2021

PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is one of the most advanced engineering polymers available today.
Belonging to the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, it is often referred to as “the king of polymers” thanks to its exceptional combination of mechanical, thermal and chemical properties, which are difficult to match with other plastics.
Because of these characteristics, PEEK is widely used in highly demanding sectors such as aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics and chemical processing, often as a direct alternative to metal alloys.
PEEK is a semi-crystalline organic thermoplastic polymer belonging to the PAEK family.
Unlike common polymers such as PLA, ABS or PETG, PEEK is designed to operate under extreme conditions, maintaining stability even when exposed to:
high temperatures
heavy mechanical loads
chemically aggressive environments
Its molecular structure gives it outstanding stability and strength, while maintaining a much lower density than metals.
PEEK combines metal-like mechanical performance with the light weight of a polymer.
Tensile strength: up to approximately 100 MPa
Density: around 1.30 g/cm³ (for comparison: aluminium alloys ≈ 2.8 g/cm³)
Continuous operating temperature: up to 250–260 °C
High HDT (Heat Deflection Temperature)
Excellent fatigue and creep resistance
Outstanding chemical resistance
The combination of high mechanical strength and low density makes PEEK an excellent candidate for metal replacement, with the added benefit of enabling complex geometries through additive manufacturing.
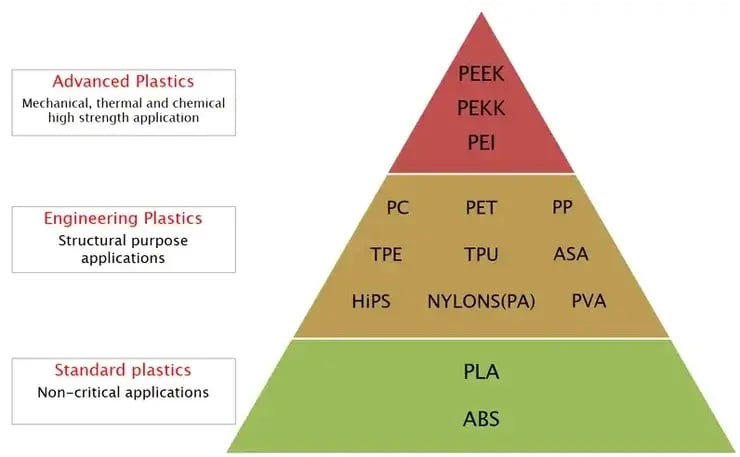
PEEK sits at the top of the engineering polymer hierarchy due to its balanced performance in:
thermal resistance
mechanical strength
dimensional stability
chemical resistance
biocompatibility
This makes it superior to most high-performance thermoplastics such as nylon, PPS or PEI when overall performance is required.
PEEK is challenging to process, but it can be successfully manufactured using industrial FDM 3D printing.
Nozzle temperature: above 400 °C
Heated chamber: at least 70 °C (often higher)
Industrial-grade printers only (not consumer machines)
These conditions are only achievable with dedicated industrial FDM systems designed specifically for high-performance polymers.
use of dedicated, easily removable support materials
elimination of traditional design constraints such as:
undercuts
internal channels
complex internal geometries
production of fully functional end-use parts, not just prototypes
PEEK can exist in two different crystalline states, which directly affect its performance.

Amber-coloured
Disordered molecular chains
Higher ductility
Better impact resistance
Lower maximum operating temperature
Ideal when:
impact resistance is required
some flexibility is beneficial
brittle behaviour must be avoided
 Semi-Crystalline PEEK
Semi-Crystalline PEEKBeige / ivory colour
More ordered molecular structure
Improved mechanical and chemical properties
Stiffer and slightly more brittle behaviour
Operating temperatures up to ~250 °C
Preferred for:
high-temperature applications
structural components
harsh operating environments
| Property | Amorphous PEEK | Semi-Crystalline PEEK |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength [MPa] | ~70 | ~100 |
| Elongation [%] | ~12 | ~9 |
| HDT (0.8 MPa) [°C] | ~145 | ~180 |
| Behaviour | More ductile | More rigid |
| Ideal use | Impact resistance | High-temperature performance |
Thanks to its performance, PEEK is used in high-value, mission-critical applications.
structural brackets
housings and covers
thermal and electrical insulation
spinal implants
prosthetics
surgical instruments
sterilisation-resistant devices
(PEEK is considered an advanced biomaterial)
components near engines and exhaust systems
vibration- and heat-resistant parts
valves
seals
components exposed to aggressive fluids
PEEK is not a universal material and should be selected when:
standard polymers are insufficient
metals are too heavy
high performance is required in compact designs
complex geometries are needed
reliability is critical
PEEK represents the pinnacle of engineering polymers.
Its ability to combine high mechanical strength, extreme thermal resistance, chemical stability and low weight makes it a powerful alternative to metal alloys in many advanced applications.
Thanks to industrial FDM 3D printing, PEEK can now be used to produce custom, complex and fully functional components, reducing weight, lead times and design constraints.
If you believe PEEK is the right material for your project, you can review the technical data sheets and instantly estimate costs by uploading your 3D file.
3 min read
Yield strength is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials, especially in engineering, structural design, CNC machining and 3D...

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
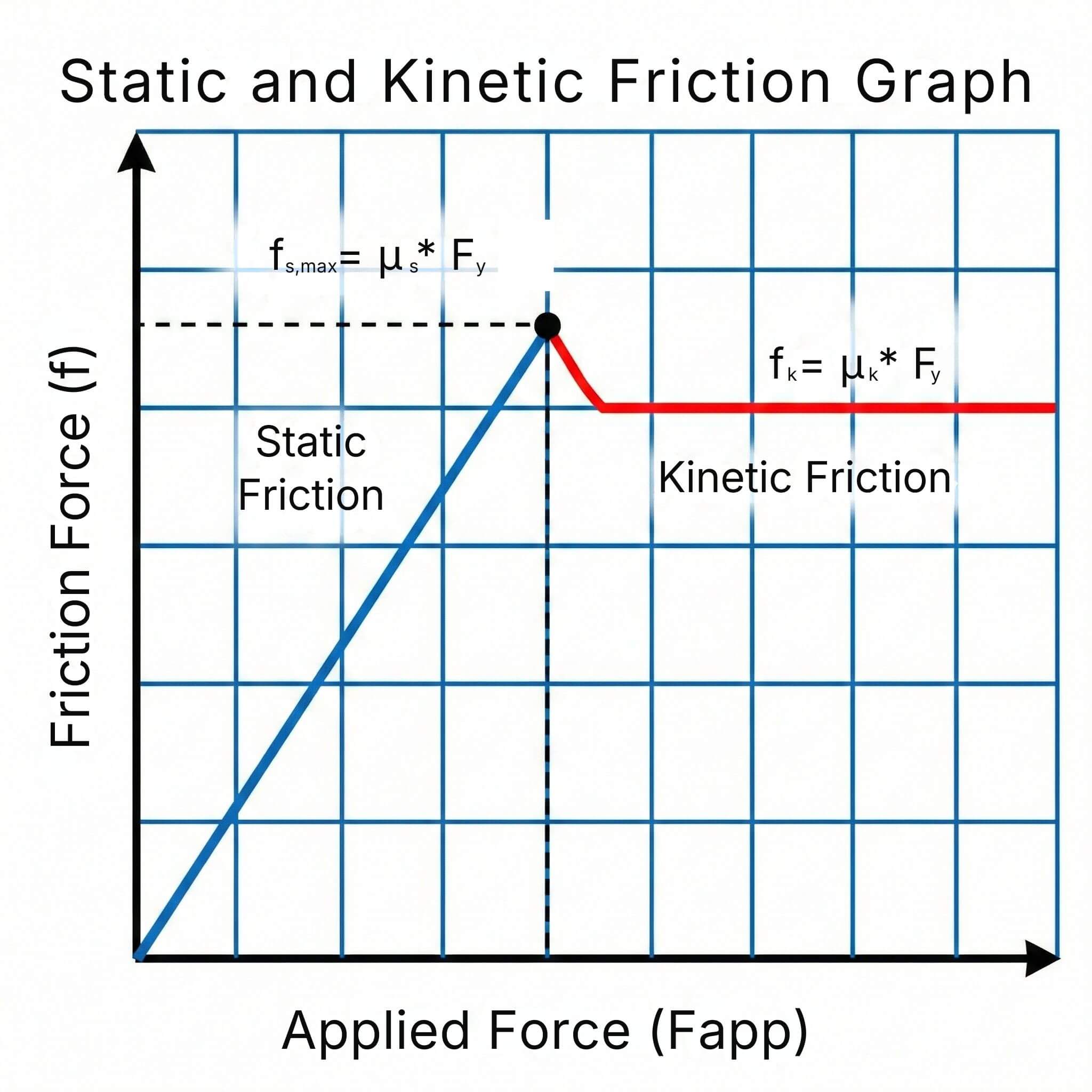
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...