4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
2 min read
![]() Weerg staff
:
Dec 30, 2025
Weerg staff
:
Dec 30, 2025
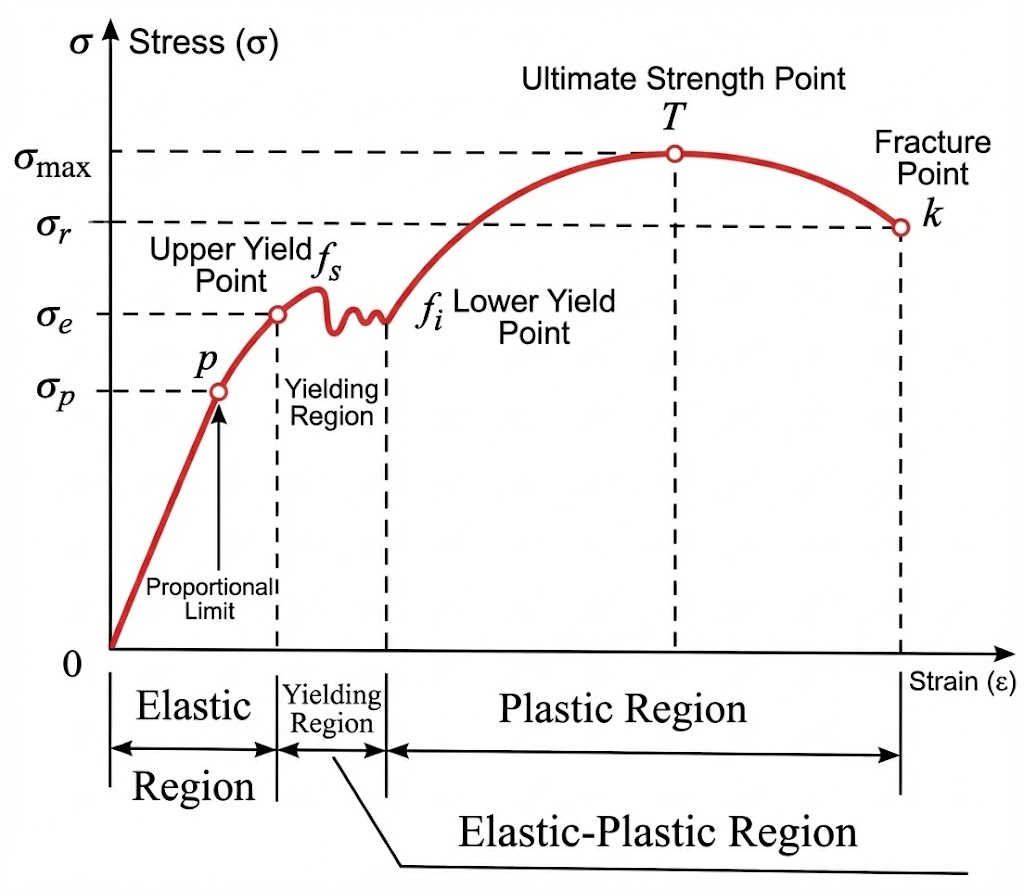
Young’s modulus, also known as the longitudinal modulus of elasticity, is one of the most important mechanical properties of materials. It is used daily in engineering, mechanical design and 3D printing to evaluate a material’s stiffness.
Understanding Young’s modulus means being able to predict how an object will react to loads, helping to avoid structural failure. In this 2026 guide we will cover the definition, formula and practical applications.
Young’s modulus (E) measures the stiffness of a material, that is, its ability to resist elastic deformation when subjected to tension or compression.
High modulus: rigid material (e.g. steel).
Low modulus: elastic material (e.g. rubber).
It describes behaviour in the elastic region: if the load is removed, the material returns to its original shape (Hooke’s law).
Young’s modulus is the ratio between stress and strain, derived from Hooke’s law:
E = σ / ε
Where:
σ (Sigma) – Stress: the applied force per unit area (measured in pascals, Pa).
ε (Epsilon) – Strain: the relative elongation with respect to the original length (dimensionless).
The unit of measurement is the pascal (Pa), but in practice the following are commonly used:
GPa (gigapascal): for metals and rigid polymers.
MPa (megapascal): for soft materials and elastomers.
A common mistake is to confuse Young’s modulus with strength.
Young’s modulus: how much a material bends under load.
Breaking load: the point at which the material fails.
A material can be very stiff but brittle (e.g. glass), or not very stiff but extremely durable (e.g. rubber).
|
Material |
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
Behavior |
|
Rubber |
0,01 - 0,1 |
Very elastic |
|
TPU (3D Printing) |
0,02 - 0,05 |
Elastic |
|
Nylon PA12 |
1,4 - 1,8 |
Flexible and tough |
|
ABS |
1,5 - 2,5 |
Moderately stiff |
|
PLA |
2,5 - 3,5 |
Stiff (but brittle) |
|
Aluminum |
~70 |
Structural stiffness |
|
Titanium |
~110 |
High specific stiffness |
|
Steel |
~200 |
Very stiff |
In Ashby charts, Young’s modulus is often related to:
density → to assess stiffness-to-weight ratio
cost → to optimise performance and budget
toughness → to avoid overly brittle materials
Typical example:
Young’s modulus vs density → selection of lightweight and stiff materials (aerospace, drones, automotive).

Young’s modulus is essential for:
It allows calculation of:
bending
elongation
elastic deflection
Fundamental for:
gears
supports
frames
mating parts
For example:
high stiffness → frames, structures
low stiffness → seals, dampers
Especially in:
drones
automotive
aerospace
In additive manufacturing, the nominal material value (from the datasheet) is not the only factor. You must also consider:
Technology: MJF and SLS offer more isotropic properties than FDM.
Orientation: in FDM, the modulus along the Z axis is often lower.
Process: Nylon PA12 printed with MJF behaves differently from injection-moulded PA12.
Young’s modulus is a material constant. Part stiffness depends on geometry.
Example: by increasing thickness or adding ribs, you can make a nylon part stiff, overcoming the intrinsic limits of the material itself.
Knowing the modulus of elasticity is vital for optimising weight and costs without risking failure.
Do you need to choose between flexibility and stiffness for your next project?
and get an instant quote with the materials best suited to your technical specifications.

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
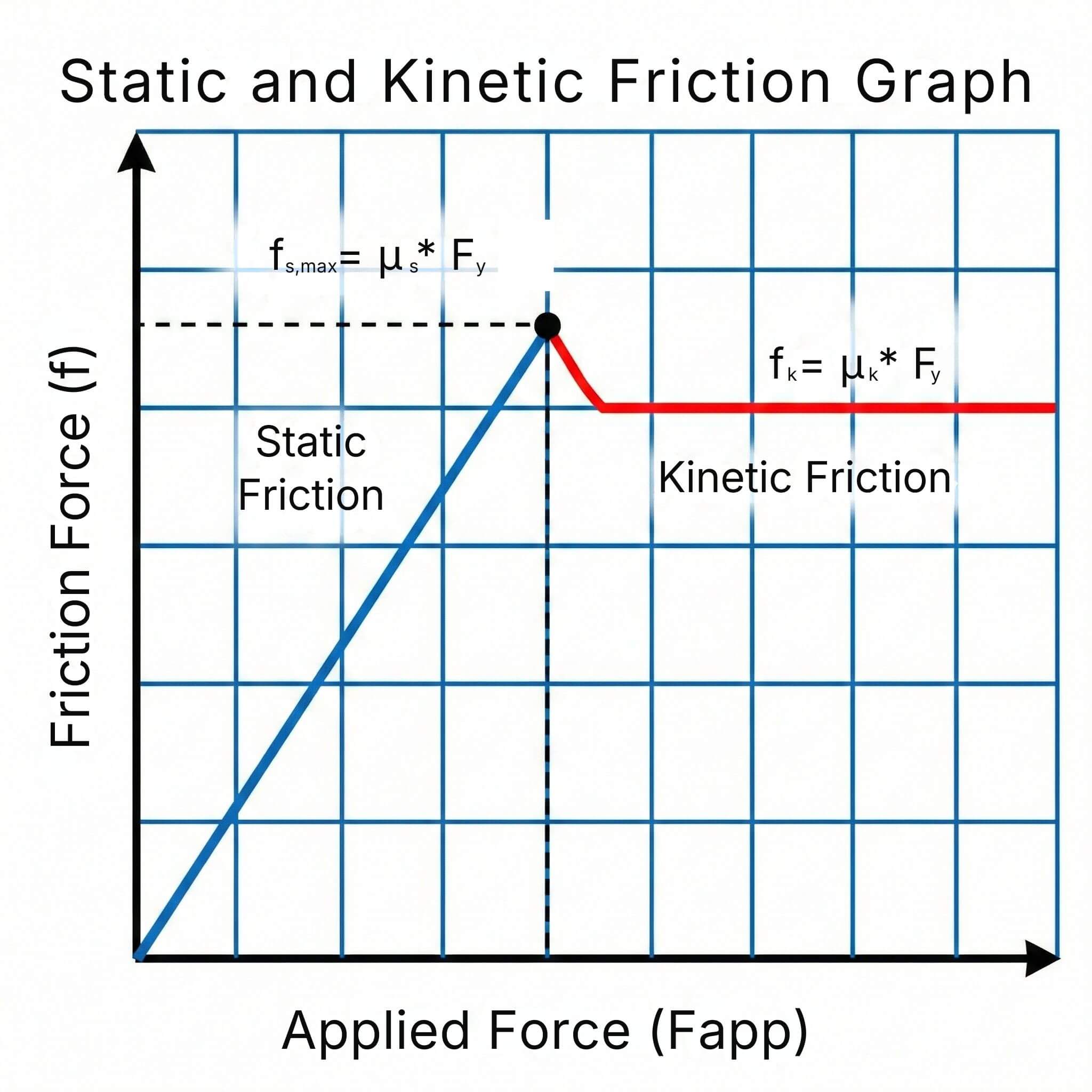
2 min read
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...