VALOI optimises production with Weerg’s PA12 3D printing
VALOI, a brand of the Finnish company Kameratori Oy and specialised in film-digitalisation systems for the home market,...
90+ 3D printers, 35+ materials and simply the best printing technologies in the world
Weerg is the Online 3D Printing Service at its best: evaluation of the 3D file or model, printing process and finishing for functional prototypes or production are ALL made in-house in our 10.000 m² factory in Italy
Discover Weerg’s 25 HP 5620 pro and their advantages
Upload your 3D file, choose material, finish and delivery date, finished.
The price appears in real time and there will be no changes, you can count on it.
No surprises or hidden costs. Easy isn't it?
At Weerg we pride ourselves on providing fast, reliable, and amazing customer service. We believe its what separates great companies from average ones.
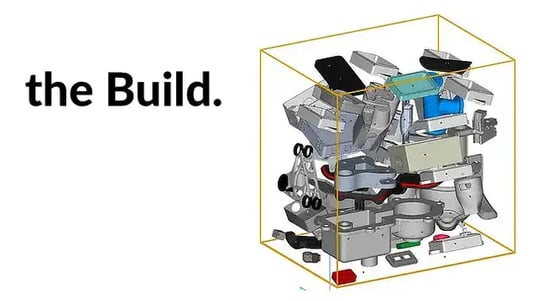
If you are a professional who prints many parts in PA12/PA11 nylon or polypropylene PP with HP Multi Jet Fusion technology, nesting on the 3D build can help you to obtain savings of up to 60%.
How? Let's see it together:
What is 3D nesting and why the 3D build will save you up to 60%?
How to nest a 3D Build? Guide
Save time, cost and hassle. Weerg is designed to enable you to take full advantage of the highest performing and most sophisticated 3D technologies without investing your time and money in hardware.
We are not resellers of other people's parts.
Because we like to live producing, not earning commissions on other people's work.
Your confidential files will not go around the world looking for the most in need supplier.
At Weerg you will be able to speak directly with whoever receives and checks your files, with the operator who produces your pieces and with whoever checks or ships them. These people produce your parts with love and all work under the same roof: the Weerg factory, Venice, Italy.
Dec 17, 2025 by Weerg staff
VALOI, a brand of the Finnish company Kameratori Oy and specialised in film-digitalisation systems for the home market,...
Dec 3, 2025 by Weerg staff
In the world of FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling) 3D printing, material selection is a key factor in determining the...
Nov 24, 2025 by Weerg staff
Weerg, a global reference in additive manufacturing and online CNC machining, collaborates with CT Pack, an Italian ...
The prices of your projects appear in real time and will not change.