4 min read
Uses of Metals: Types, Classifications and Applications
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
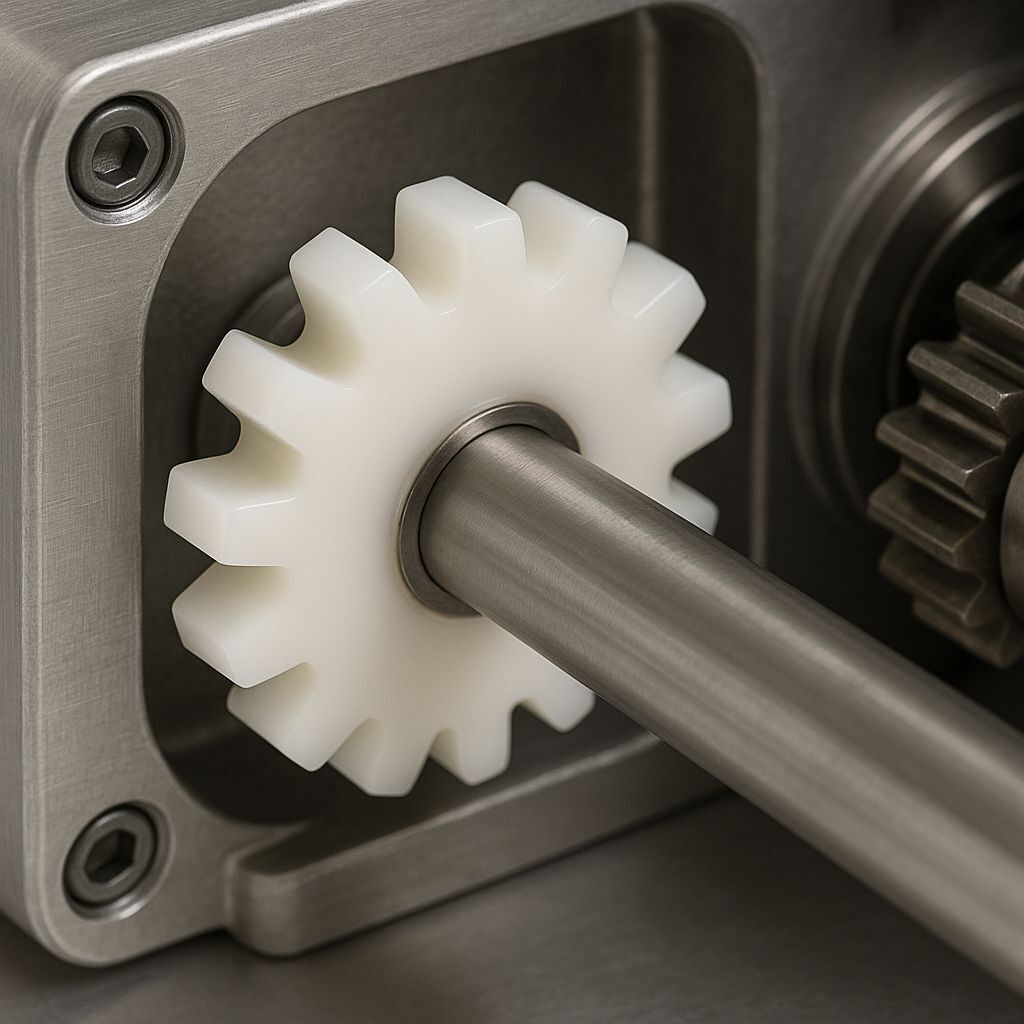

POM‑C, also known as polyoxymethylene copolymer or acetal resin, is a high‑performance engineering plastic material. Used in mechanical, fluid‑handling and electromechanical applications, the POM‑C material offers an ideal balance of stiffness, smooth sliding (low friction), dimensional stability and excellent machinability.
In this guide updated to 2026, you will learn what POM‑C plastic is, its technical properties, key applications, advantages versus other engineering polymers, and how to process it via CNC machining, injection moulding and additive manufacturing.
POM (polyoxymethylene) is a semi‑crystalline thermoplastic belonging to the acetal resin family. There are two main variants:
POM‑H (homopolymer) — higher stiffness and tensile strength.
POM‑C (copolymer) — better thermal stability and hydrolysis resistance.
POM‑C material is the preferred choice in humid or chemically aggressive environments thanks to its durability, wear resistance and fatigue performance.

Easy turning and milling
Tight tolerances achievable
Excellent surface finish
Fast cycle times
Predictable shrinkage
Care required with venting and mould humidity
POM‑C plastic withstands oils, greases, fuels, solvents and industrial cleaners, but is sensitive to UV radiation and strong oxidising acids. For outdoor use, consider stabilisers or appropriate surface treatments.
Use POM‑C material when you need:
Do you need white or black POM-C parts for CNC?
Get an instant, free quote for your acetal resin POM‑C production now

4 min read
Metals are among the most important and widely used materials by humankind.From prehistory to Industry 4.0, they have supported technological...
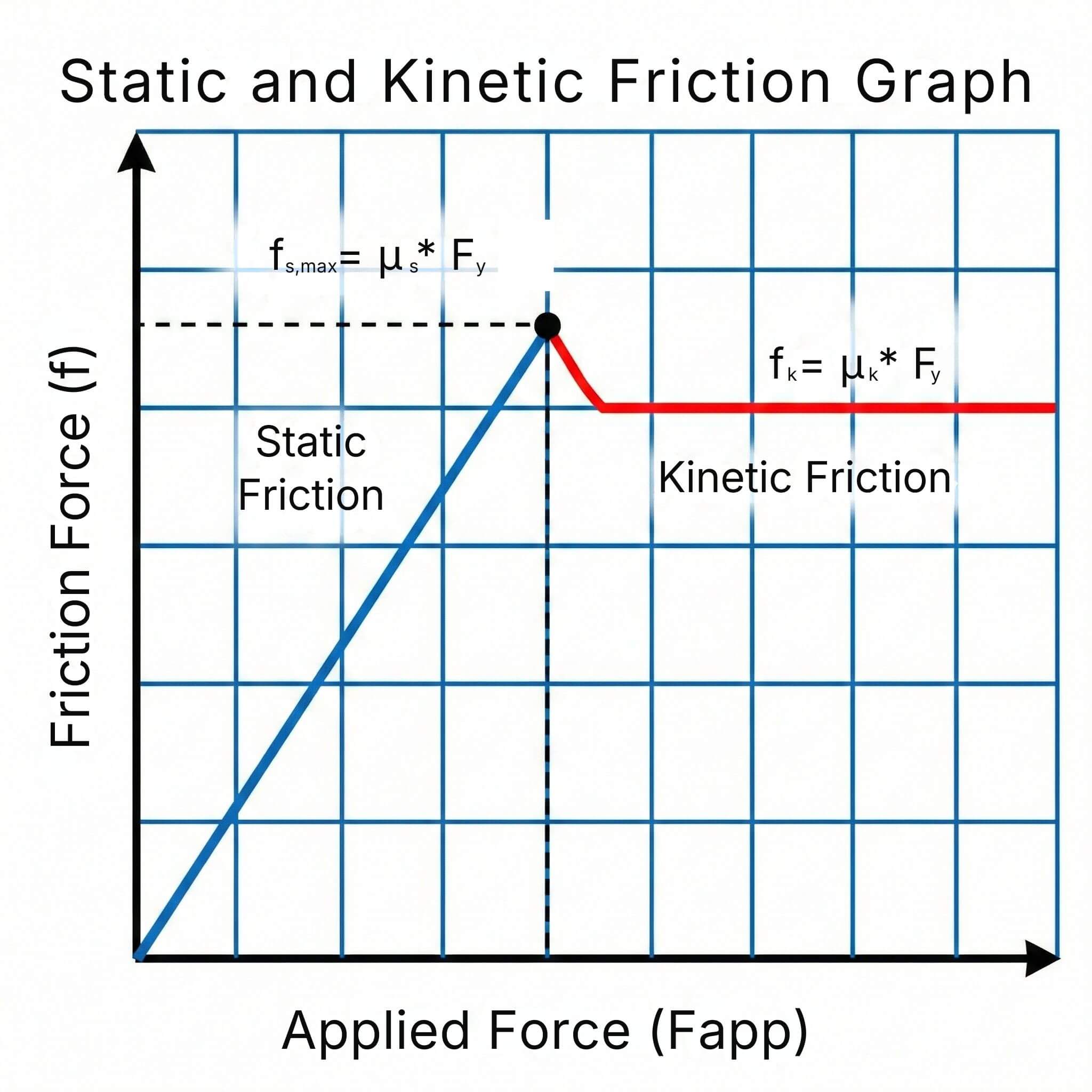
2 min read
The coefficient of friction (μ) measures the resistance to sliding between two surfaces in contact. It is a key parameter in mechanical design...

3 min read
The CBAM regulation (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism) represents one of the key pillars of the European strategy for industrial decarbonisation...